[Categorical data analysis] Assignment(2)
패키지 설치된 패키지 접기/펼치기 버튼
library('kableExtra')
library("dplyr")
library("ROCR")
library("glmtoolbox")
library("ggplot2")
library("predtools")
library("gbm")
library("foreign")
library("VGAM")
Q-1
auto <- read.csv("C:/Biostat/Categorical data analysis/Assignment 2/Auto.csv")
head(auto)%>%
kable(caption = "Auto dataset",booktabs = TRUE, valign = 't')%>%
kable_styling(bootstrap_options = c("striped", "hover", "condensed", "responsive"))
| mpg | cylinders | displacement | horsepower | weight | acceleration | year | origin | name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18 | 8 | 307 | 130 | 3504 | 12.0 | 70 | 1 | chevrolet chevelle malibu |
| 15 | 8 | 350 | 165 | 3693 | 11.5 | 70 | 1 | buick skylark 320 |
| 18 | 8 | 318 | 150 | 3436 | 11.0 | 70 | 1 | plymouth satellite |
| 16 | 8 | 304 | 150 | 3433 | 12.0 | 70 | 1 | amc rebel sst |
| 17 | 8 | 302 | 140 | 3449 | 10.5 | 70 | 1 | ford torino |
| 15 | 8 | 429 | 198 | 4341 | 10.0 | 70 | 1 | ford galaxie 500 |
str(auto)
## 'data.frame': 397 obs. of 9 variables:
## $ mpg : num 18 15 18 16 17 15 14 14 14 15 ...
## $ cylinders : int 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 ...
## $ displacement: num 307 350 318 304 302 429 454 440 455 390 ...
## $ horsepower : chr "130" "165" "150" "150" ...
## $ weight : int 3504 3693 3436 3433 3449 4341 4354 4312 4425 3850 ...
## $ acceleration: num 12 11.5 11 12 10.5 10 9 8.5 10 8.5 ...
## $ year : int 70 70 70 70 70 70 70 70 70 70 ...
## $ origin : int 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 ...
## $ name : chr "chevrolet chevelle malibu" "buick skylark 320" "plymouth satellite" "amc rebel sst" ...
mpg
miles per galloncylinders
Number of cylinders between 4 and 8displacement
Engine displacement (cu. inches)horsepower
Engine horsepowerweight
Vehicle weight (lbs.)acceleration
Time to accelerate from 0 to 60 mph (sec.)year
Model year (modulo 100)origin
Origin of car (1. American, 2. European, 3. Japanese)name
Vehicle name
auto$horsepower <- as.integer(auto$horsepower)
auto$origin <- as.factor(auto$origin)
table(is.na(auto$horsepower))
##
## FALSE TRUE
## 392 5
auto1 <- na.omit(auto)
table(is.na(auto1$horsepower))
##
## FALSE
## 392
summary(auto1$mpg)[3]
## Median
## 22.75
auto1$mpg_G[auto1$mpg>22.75]='1'
auto1$mpg_G[auto1$mpg<=22.75]='0'
#70년도 기준으로
auto1$year_70 <- auto1$year-70
auto1$mpg_G <- as.integer(auto1$mpg_G)
attach(auto1)
데이터에서 5개의 결측치를 확인하여 제거하였고 mpg variable을 median을 기준으로 두 그룹으로 나누어 binary indicator variable로 지정하였다. (i.e > median (Y=1) vs <= median (Y=0)).
year변수는 해석의 용이성을 위하여 70년도를 기준으로 잡아서 변환하였다.
Q-1 1)
풀모델에서 각 변수마다 Coefficients를 확인하여 p-value가 가장 큰 값부터 하나씩 제거하여 model을 생성하겠다.
fit.cloglog <- glm(mpg_G ~ cylinders + displacement + horsepower + weight + acceleration + year_70 + origin, family=binomial(link=cloglog), data=auto1)
summary(fit.cloglog)
##
## Call:
## glm(formula = mpg_G ~ cylinders + displacement + horsepower +
## weight + acceleration + year_70 + origin, family = binomial(link = cloglog),
## data = auto1)
##
## Deviance Residuals:
## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
## -2.31665 -0.17396 -0.00165 0.02882 2.90461
##
## Coefficients:
## Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
## (Intercept) 9.3079844 2.2119023 4.208 2.57e-05 ***
## cylinders -0.0367593 0.2654776 -0.138 0.889873
## displacement -0.0002667 0.0081791 -0.033 0.973989
## horsepower -0.0309802 0.0155023 -1.998 0.045671 *
## weight -0.0029715 0.0008061 -3.686 0.000228 ***
## acceleration -0.0201927 0.0853585 -0.237 0.812996
## year_70 0.2979199 0.0490991 6.068 1.30e-09 ***
## origin2 0.7625428 0.4299018 1.774 0.076103 .
## origin3 0.1938729 0.4028236 0.481 0.630314
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## (Dispersion parameter for binomial family taken to be 1)
##
## Null deviance: 543.43 on 391 degrees of freedom
## Residual deviance: 151.76 on 383 degrees of freedom
## AIC: 169.76
##
## Number of Fisher Scoring iterations: 10
#displacement 제거 (엔진 배기량)
fit.cloglog1 <- glm(mpg_G ~ cylinders + horsepower + weight + acceleration + year_70 + origin, family=binomial(link=cloglog), data=auto1)
summary(fit.cloglog1)
##
## Call:
## glm(formula = mpg_G ~ cylinders + horsepower + weight + acceleration +
## year_70 + origin, family = binomial(link = cloglog), data = auto1)
##
## Deviance Residuals:
## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
## -2.32315 -0.17398 -0.00167 0.02885 2.90007
##
## Coefficients:
## Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
## (Intercept) 9.3263971 2.1292083 4.380 1.19e-05 ***
## cylinders -0.0432813 0.1899260 -0.228 0.8197
## horsepower -0.0309773 0.0154855 -2.000 0.0455 *
## weight -0.0029847 0.0006461 -4.620 3.84e-06 ***
## acceleration -0.0199970 0.0849466 -0.235 0.8139
## year_70 0.2980555 0.0480496 6.203 5.54e-10 ***
## origin2 0.7706041 0.3491559 2.207 0.0273 *
## origin3 0.2002353 0.3544489 0.565 0.5721
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## (Dispersion parameter for binomial family taken to be 1)
##
## Null deviance: 543.43 on 391 degrees of freedom
## Residual deviance: 151.76 on 384 degrees of freedom
## AIC: 167.76
##
## Number of Fisher Scoring iterations: 10
#cylinders 제거 (실린더 수)
fit.cloglog2 <- glm(mpg_G ~ horsepower + weight + acceleration + year_70 + origin, family=binomial(link=cloglog), data=auto1)
summary(fit.cloglog2)
##
## Call:
## glm(formula = mpg_G ~ horsepower + weight + acceleration + year_70 +
## origin, family = binomial(link = cloglog), data = auto1)
##
## Deviance Residuals:
## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
## -2.32191 -0.17203 -0.00155 0.02775 2.89262
##
## Coefficients:
## Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
## (Intercept) 9.3682686 2.1329876 4.392 1.12e-05 ***
## horsepower -0.0316641 0.0151936 -2.084 0.0372 *
## weight -0.0030658 0.0005504 -5.570 2.55e-08 ***
## acceleration -0.0189498 0.0849107 -0.223 0.8234
## year_70 0.3000314 0.0468994 6.397 1.58e-10 ***
## origin2 0.8033144 0.3298878 2.435 0.0149 *
## origin3 0.2222345 0.3479796 0.639 0.5231
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## (Dispersion parameter for binomial family taken to be 1)
##
## Null deviance: 543.43 on 391 degrees of freedom
## Residual deviance: 151.81 on 385 degrees of freedom
## AIC: 165.81
##
## Number of Fisher Scoring iterations: 10
#acceleration 제거 (가속 시간)
fit.cloglog3 <- glm(mpg_G ~ horsepower + weight + year_70 + origin, family=binomial(link=cloglog), data=auto1)
summary(fit.cloglog3)
##
## Call:
## glm(formula = mpg_G ~ horsepower + weight + year_70 + origin,
## family = binomial(link = cloglog), data = auto1)
##
## Deviance Residuals:
## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
## -2.31451 -0.17472 -0.00163 0.02704 2.87934
##
## Coefficients:
## Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
## (Intercept) 8.9793062 1.2985006 6.915 4.67e-12 ***
## horsepower -0.0292603 0.0104085 -2.811 0.00494 **
## weight -0.0031201 0.0004831 -6.458 1.06e-10 ***
## year_70 0.3010277 0.0468524 6.425 1.32e-10 ***
## origin2 0.8004047 0.3272749 2.446 0.01446 *
## origin3 0.2244828 0.3473603 0.646 0.51812
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## (Dispersion parameter for binomial family taken to be 1)
##
## Null deviance: 543.43 on 391 degrees of freedom
## Residual deviance: 151.86 on 386 degrees of freedom
## AIC: 163.86
##
## Number of Fisher Scoring iterations: 10
#origin 제거 (자동차의 원산지)
fit.cloglog4 <- glm(mpg_G ~ horsepower + weight + year_70, family=binomial(link=cloglog), data=auto1)
summary(fit.cloglog4)
##
## Call:
## glm(formula = mpg_G ~ horsepower + weight + year_70, family = binomial(link = cloglog),
## data = auto1)
##
## Deviance Residuals:
## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
## -2.28842 -0.19538 -0.00203 0.04135 2.80384
##
## Coefficients:
## Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
## (Intercept) 9.1880300 1.1860338 7.747 9.42e-15 ***
## horsepower -0.0278086 0.0095726 -2.905 0.00367 **
## weight -0.0031302 0.0004389 -7.132 9.91e-13 ***
## year_70 0.2860917 0.0453716 6.306 2.87e-10 ***
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## (Dispersion parameter for binomial family taken to be 1)
##
## Null deviance: 543.43 on 391 degrees of freedom
## Residual deviance: 157.91 on 388 degrees of freedom
## AIC: 165.91
##
## Number of Fisher Scoring iterations: 9
link function을 Complementaty Log-Log Link를 사용하여 4개의 모형이 생성하였다.
4가지의 생성된 모델들간에 Deviance로 비교하여 “deviance(작은 모델)-deviance(큰 모델)”에서 deviance가 커서 유의하게 나오면 큰 모델, 유의하지 않게 나오면 작은 모델을 선택하겠다.
anova(fit.cloglog1,fit.cloglog, test="LR")
## Analysis of Deviance Table
##
## Model 1: mpg_G ~ cylinders + horsepower + weight + acceleration + year_70 +
## origin
## Model 2: mpg_G ~ cylinders + displacement + horsepower + weight + acceleration +
## year_70 + origin
## Resid. Df Resid. Dev Df Deviance Pr(>Chi)
## 1 384 151.76
## 2 383 151.76 1 0.0010984 0.9736
anova(fit.cloglog2,fit.cloglog1, test="LR")
## Analysis of Deviance Table
##
## Model 1: mpg_G ~ horsepower + weight + acceleration + year_70 + origin
## Model 2: mpg_G ~ cylinders + horsepower + weight + acceleration + year_70 +
## origin
## Resid. Df Resid. Dev Df Deviance Pr(>Chi)
## 1 385 151.81
## 2 384 151.76 1 0.049787 0.8234
anova(fit.cloglog3,fit.cloglog2, test="LR")
## Analysis of Deviance Table
##
## Model 1: mpg_G ~ horsepower + weight + year_70 + origin
## Model 2: mpg_G ~ horsepower + weight + acceleration + year_70 + origin
## Resid. Df Resid. Dev Df Deviance Pr(>Chi)
## 1 386 151.86
## 2 385 151.81 1 0.049788 0.8234
anova(fit.cloglog4,fit.cloglog3, test="LR")
## Analysis of Deviance Table
##
## Model 1: mpg_G ~ horsepower + weight + year_70
## Model 2: mpg_G ~ horsepower + weight + year_70 + origin
## Resid. Df Resid. Dev Df Deviance Pr(>Chi)
## 1 388 157.91
## 2 386 151.86 2 6.0564 0.0484 *
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
\[\begin{align} &log(-log(1-P(Y=1)))=8.9793062-0.0292603*horsepower-0.0031201*weight+0.3010277*year_{70} \\ &log(-log(1-P(Y=1)))=8.9793062-0.0292603*horsepower-0.0031201*weight+0.3010277*year_{70}+0.8004047*origin2 \\ &log(-log(1-P(Y=1)))=8.9793062-0.0292603*horsepower-0.0031201*weight+0.3010277*year_{70}+0.2244828*origin3 \end{align}\]fit.cloglog3 선택
fit.cloglog3 에서 horsepower, weight, year_70, origin2 변수가 유의수준 0.05하에 유의하게 나왔으며 확률로 변환 하면 다음과 같이 식이 정리된다.
\[P(Y=1)=1-e^{-e^{8.9793062-0.0292603*horsepower-0.0031201*weight+0.3010277*year_{70}}}\] \[해석: \ American에서 \ 제조된 \ 차량의 \ 경우 \ mpg가 \ 22.75(median)보다 \ 작을 \ 확률은 \ horsepower가 \ 10 \ 증가할 \ 때 e^{-0.0292603*10}=0.746 \ power(거듭제곱) \ 된다.\]origin이 American일 경우
\[P(Y=1)=1-e^{-e^{8.9793062-0.0292603*horsepower-0.0031201*weight+0.3010277*year_{70}+0.8004047*origin2}}\] \[해석: \ European에서 \ 제조된 \ 차량의 \ 경우 \ mpg가 \ 22.75(median)보다 \ 작을 \ 확률은 \ horsepower가 \ 10 \ 증가할 \ 때 \ e^{-0.0292603*10+0.8004047}=1.66 \ power(거듭제곱) \ 된다.\]origin이 European일 경우
차량의 제조사가 American일 때 mpg가 22.75(median)보다 작을 확률은 horsepower가 증가할 때 0.746제곱 줄어들지만 European일 때 horsepower가 증가하면 1.66제곱 증가한다.
Q-1 2)
fit.probit <- glm(mpg_G ~ cylinders + displacement + horsepower + weight + acceleration + year_70 + origin, family=binomial(link=probit), data=auto1)
summary(fit.probit)
##
## Call:
## glm(formula = mpg_G ~ cylinders + displacement + horsepower +
## weight + acceleration + year_70 + origin, family = binomial(link = probit),
## data = auto1)
##
## Deviance Residuals:
## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
## -2.43580 -0.05453 0.00016 0.16409 3.11073
##
## Coefficients:
## Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
## (Intercept) 8.0579048 1.9720873 4.086 4.39e-05 ***
## cylinders -0.1550644 0.2405084 -0.645 0.519
## displacement 0.0092172 0.0072574 1.270 0.204
## horsepower -0.0216091 0.0136622 -1.582 0.114
## weight -0.0032621 0.0007368 -4.428 9.53e-06 ***
## acceleration 0.0260957 0.0792587 0.329 0.742
## year_70 0.2792523 0.0451645 6.183 6.29e-10 ***
## origin2 1.0796508 0.4243628 2.544 0.011 *
## origin3 0.5947097 0.3956339 1.503 0.133
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## (Dispersion parameter for binomial family taken to be 1)
##
## Null deviance: 543.43 on 391 degrees of freedom
## Residual deviance: 152.61 on 383 degrees of freedom
## AIC: 170.61
##
## Number of Fisher Scoring iterations: 9
#acceleration 제거 (가속 시간)
fit.probit1 <- glm(mpg_G ~ cylinders + displacement + horsepower + weight + year_70 + origin, family=binomial(link=probit), data=auto1)
summary(fit.probit1)
##
## Call:
## glm(formula = mpg_G ~ cylinders + displacement + horsepower +
## weight + year_70 + origin, family = binomial(link = probit),
## data = auto1)
##
## Deviance Residuals:
## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
## -2.44380 -0.04933 0.00017 0.16522 3.14974
##
## Coefficients:
## Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
## (Intercept) 8.5448670 1.3394995 6.379 1.78e-10 ***
## cylinders -0.1539979 0.2406922 -0.640 0.5223
## displacement 0.0091242 0.0072476 1.259 0.2081
## horsepower -0.0248235 0.0096642 -2.569 0.0102 *
## weight -0.0031706 0.0006723 -4.716 2.40e-06 ***
## year_70 0.2783613 0.0450383 6.181 6.39e-10 ***
## origin2 1.0828513 0.4248124 2.549 0.0108 *
## origin3 0.5940991 0.3951464 1.503 0.1327
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## (Dispersion parameter for binomial family taken to be 1)
##
## Null deviance: 543.43 on 391 degrees of freedom
## Residual deviance: 152.72 on 384 degrees of freedom
## AIC: 168.72
##
## Number of Fisher Scoring iterations: 9
#cylinders 제거 (실린더 수)
fit.probit2 <- glm(mpg_G ~ displacement + horsepower + weight + year_70 + origin, family=binomial(link=probit), data=auto1)
summary(fit.probit2)
##
## Call:
## glm(formula = mpg_G ~ displacement + horsepower + weight + year_70 +
## origin, family = binomial(link = probit), data = auto1)
##
## Deviance Residuals:
## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
## -2.3623 -0.0479 0.0001 0.1650 3.2313
##
## Coefficients:
## Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
## (Intercept) 8.3199497 1.2922606 6.438 1.21e-10 ***
## displacement 0.0059549 0.0050022 1.190 0.23387
## horsepower -0.0259648 0.0095002 -2.733 0.00627 **
## weight -0.0031280 0.0006628 -4.720 2.36e-06 ***
## year_70 0.2768439 0.0445481 6.214 5.15e-10 ***
## origin2 1.0452355 0.4187476 2.496 0.01256 *
## origin3 0.5439216 0.3828527 1.421 0.15540
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## (Dispersion parameter for binomial family taken to be 1)
##
## Null deviance: 543.43 on 391 degrees of freedom
## Residual deviance: 153.14 on 385 degrees of freedom
## AIC: 167.14
##
## Number of Fisher Scoring iterations: 9
#displacement 제거 (엔진 배기량)
fit.probit3 <- glm(mpg_G ~ horsepower + weight + year_70 + origin, family=binomial(link=probit), data=auto1)
summary(fit.probit3)
##
## Call:
## glm(formula = mpg_G ~ horsepower + weight + year_70 + origin,
## family = binomial(link = probit), data = auto1)
##
## Deviance Residuals:
## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
## -2.2366 -0.0642 0.0005 0.1722 3.4432
##
## Coefficients:
## Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
## (Intercept) 7.3919689 1.0133564 7.295 3.00e-13 ***
## horsepower -0.0224948 0.0089681 -2.508 0.0121 *
## weight -0.0024853 0.0003815 -6.515 7.28e-11 ***
## year_70 0.2584634 0.0399842 6.464 1.02e-10 ***
## origin2 0.7017442 0.2910427 2.411 0.0159 *
## origin3 0.3197478 0.3286180 0.973 0.3305
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## (Dispersion parameter for binomial family taken to be 1)
##
## Null deviance: 543.43 on 391 degrees of freedom
## Residual deviance: 154.68 on 386 degrees of freedom
## AIC: 166.68
##
## Number of Fisher Scoring iterations: 9
#origin 제거 (자동차의 원산지)
fit.probit4 <- glm(mpg_G ~ horsepower + weight + year_70, family=binomial(link=probit), data=auto1)
summary(fit.probit4)
##
## Call:
## glm(formula = mpg_G ~ horsepower + weight + year_70, family = binomial(link = probit),
## data = auto1)
##
## Deviance Residuals:
## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
## -2.1653 -0.0787 0.0006 0.1894 3.3443
##
## Coefficients:
## Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
## (Intercept) 7.8614752 0.9405796 8.358 < 2e-16 ***
## horsepower -0.0208243 0.0082271 -2.531 0.0114 *
## weight -0.0026004 0.0003403 -7.641 2.15e-14 ***
## year_70 0.2452354 0.0387544 6.328 2.48e-10 ***
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## (Dispersion parameter for binomial family taken to be 1)
##
## Null deviance: 543.43 on 391 degrees of freedom
## Residual deviance: 160.65 on 388 degrees of freedom
## AIC: 168.65
##
## Number of Fisher Scoring iterations: 8
link function을 Probit Link를 사용하여 4개의 모형이 생성하였다.
4가지의 생성된 모델들간에 Deviance로 비교하여 “deviance(작은 모델)-deviance(큰 모델)”에서 deviance가 커서 유의하게 나오면 큰 모델, 유의하지 않게 나오면 작은 모델을 선택하겠다.
anova(fit.probit1,fit.probit, test="LR")
## Analysis of Deviance Table
##
## Model 1: mpg_G ~ cylinders + displacement + horsepower + weight + year_70 +
## origin
## Model 2: mpg_G ~ cylinders + displacement + horsepower + weight + acceleration +
## year_70 + origin
## Resid. Df Resid. Dev Df Deviance Pr(>Chi)
## 1 384 152.72
## 2 383 152.61 1 0.1109 0.7391
anova(fit.probit2,fit.probit1, test="LR")
## Analysis of Deviance Table
##
## Model 1: mpg_G ~ displacement + horsepower + weight + year_70 + origin
## Model 2: mpg_G ~ cylinders + displacement + horsepower + weight + year_70 +
## origin
## Resid. Df Resid. Dev Df Deviance Pr(>Chi)
## 1 385 153.14
## 2 384 152.72 1 0.41785 0.518
anova(fit.probit3,fit.probit2, test="LR")
## Analysis of Deviance Table
##
## Model 1: mpg_G ~ horsepower + weight + year_70 + origin
## Model 2: mpg_G ~ displacement + horsepower + weight + year_70 + origin
## Resid. Df Resid. Dev Df Deviance Pr(>Chi)
## 1 386 154.68
## 2 385 153.14 1 1.5468 0.2136
anova(fit.probit4,fit.probit3, test="LR")
## Analysis of Deviance Table
##
## Model 1: mpg_G ~ horsepower + weight + year_70
## Model 2: mpg_G ~ horsepower + weight + year_70 + origin
## Resid. Df Resid. Dev Df Deviance Pr(>Chi)
## 1 388 160.65
## 2 386 154.68 2 5.9629 0.05072 .
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
\[\begin{align} &{\Phi}^{-1}(P(Y=1))=7.8614752-0.0208243*horsepower-0.0026004*weight+0.2452354*year_{70} \\ \end{align}\]fit.probit4 선택
\[P(Y=1)=\Phi(7.8614752-0.0208243*horsepower-0.0026004*weight+0.2452354*year_{70})\] \[해석: \ horsepower가 \ 10증가하면 \ 10(-0.0208243) \approx \ -0.2 \ standard \ deviations \ 만큼 \ E(y^*)의 \ SE가 \ 증감한다.\]fit.probit4 에서 horsepower, weight, year_70 변수가 유의수준 0.05하에 유의하게 나왔으며 확률로 변환 하면 다음과 같이 식이 정리된다.
Q-1 3)
fit.logit <- glm(mpg_G ~ cylinders + displacement + horsepower + weight + acceleration + year_70 + origin, family=binomial(link=logit), data=auto1)
summary(fit.logit)
##
## Call:
## glm(formula = mpg_G ~ cylinders + displacement + horsepower +
## weight + acceleration + year_70 + origin, family = binomial(link = logit),
## data = auto1)
##
## Deviance Residuals:
## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
## -2.44937 -0.08809 0.00577 0.19315 3.03363
##
## Coefficients:
## Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
## (Intercept) 15.243636 3.739637 4.076 4.58e-05 ***
## cylinders -0.264169 0.439645 -0.601 0.5479
## displacement 0.015568 0.013658 1.140 0.2543
## horsepower -0.043081 0.024621 -1.750 0.0802 .
## weight -0.005762 0.001376 -4.187 2.83e-05 ***
## acceleration 0.012939 0.142921 0.091 0.9279
## year_70 0.495635 0.086155 5.753 8.78e-09 ***
## origin2 1.971277 0.785573 2.509 0.0121 *
## origin3 1.102741 0.713768 1.545 0.1224
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## (Dispersion parameter for binomial family taken to be 1)
##
## Null deviance: 543.43 on 391 degrees of freedom
## Residual deviance: 152.30 on 383 degrees of freedom
## AIC: 170.3
##
## Number of Fisher Scoring iterations: 8
#acceleration 제거 (가속 시간)
fit.logit1 <- glm(mpg_G ~ cylinders + displacement + horsepower + weight + year_70 + origin, family=binomial(link=logit), data=auto1)
summary(fit.logit1)
##
## Call:
## glm(formula = mpg_G ~ cylinders + displacement + horsepower +
## weight + year_70 + origin, family = binomial(link = logit),
## data = auto1)
##
## Deviance Residuals:
## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
## -2.45068 -0.08654 0.00577 0.19126 3.04322
##
## Coefficients:
## Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
## (Intercept) 15.489516 2.585437 5.991 2.08e-09 ***
## cylinders -0.264722 0.440013 -0.602 0.5474
## displacement 0.015491 0.013651 1.135 0.2564
## horsepower -0.044638 0.017644 -2.530 0.0114 *
## weight -0.005716 0.001278 -4.473 7.70e-06 ***
## year_70 0.495092 0.085959 5.760 8.43e-09 ***
## origin2 1.971049 0.785790 2.508 0.0121 *
## origin3 1.099965 0.712968 1.543 0.1229
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## (Dispersion parameter for binomial family taken to be 1)
##
## Null deviance: 543.43 on 391 degrees of freedom
## Residual deviance: 152.31 on 384 degrees of freedom
## AIC: 168.31
##
## Number of Fisher Scoring iterations: 8
#cylinders 제거 (실린더 수)
fit.logit2 <- glm(mpg_G ~ displacement + horsepower + weight + year_70 + origin, family=binomial(link=logit), data=auto1)
summary(fit.logit2)
##
## Call:
## glm(formula = mpg_G ~ displacement + horsepower + weight + year_70 +
## origin, family = binomial(link = logit), data = auto1)
##
## Deviance Residuals:
## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
## -2.37243 -0.08310 0.00549 0.19380 3.11093
##
## Coefficients:
## Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
## (Intercept) 15.090348 2.488134 6.065 1.32e-09 ***
## displacement 0.009480 0.009281 1.021 0.30707
## horsepower -0.047007 0.017330 -2.712 0.00668 **
## weight -0.005579 0.001248 -4.472 7.75e-06 ***
## year_70 0.488489 0.084269 5.797 6.76e-09 ***
## origin2 1.876667 0.768332 2.443 0.01459 *
## origin3 0.981779 0.681971 1.440 0.14997
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## (Dispersion parameter for binomial family taken to be 1)
##
## Null deviance: 543.43 on 391 degrees of freedom
## Residual deviance: 152.68 on 385 degrees of freedom
## AIC: 166.68
##
## Number of Fisher Scoring iterations: 8
#displacement 제거 (엔진 배기량)
fit.logit3 <- glm(mpg_G ~ horsepower + weight + year_70 + origin, family=binomial(link=logit), data=auto1)
summary(fit.logit3)
##
## Call:
## glm(formula = mpg_G ~ horsepower + weight + year_70 + origin,
## family = binomial(link = logit), data = auto1)
##
## Deviance Residuals:
## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
## -2.2675 -0.0943 0.0080 0.2007 3.2653
##
## Coefficients:
## Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
## (Intercept) 13.796380 2.008420 6.869 6.45e-12 ***
## horsepower -0.042209 0.016441 -2.567 0.0103 *
## weight -0.004607 0.000734 -6.276 3.47e-10 ***
## year_70 0.457663 0.075997 6.022 1.72e-09 ***
## origin2 1.335225 0.529879 2.520 0.0117 *
## origin3 0.628677 0.580123 1.084 0.2785
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## (Dispersion parameter for binomial family taken to be 1)
##
## Null deviance: 543.43 on 391 degrees of freedom
## Residual deviance: 153.73 on 386 degrees of freedom
## AIC: 165.73
##
## Number of Fisher Scoring iterations: 8
#origin 제거 (자동차의 원산지)
fit.logit4 <- glm(mpg_G ~ horsepower + weight + year_70, family=binomial(link=logit), data=auto1)
summary(fit.logit4)
##
## Call:
## glm(formula = mpg_G ~ horsepower + weight + year_70, family = binomial(link = logit),
## data = auto1)
##
## Deviance Residuals:
## Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
## -2.18128 -0.11495 0.00957 0.21602 3.15565
##
## Coefficients:
## Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
## (Intercept) 14.3535577 1.8645823 7.698 1.38e-14 ***
## horsepower -0.0381252 0.0148566 -2.566 0.0103 *
## weight -0.0047206 0.0006539 -7.219 5.22e-13 ***
## year_70 0.4277879 0.0721903 5.926 3.11e-09 ***
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## (Dispersion parameter for binomial family taken to be 1)
##
## Null deviance: 543.43 on 391 degrees of freedom
## Residual deviance: 160.58 on 388 degrees of freedom
## AIC: 168.58
##
## Number of Fisher Scoring iterations: 8
link function을 Logit Link를 사용하여 4개의 모형이 생성하였다.
4가지의 생성된 모델들간에 Deviance로 비교하여 “deviance(작은 모델)-deviance(큰 모델)”에서 deviance가 커서 유의하게 나오면 큰 모델, 유의하지 않게 나오면 작은 모델을 선택하겠다.
anova(fit.logit1,fit.logit, test="LR")
## Analysis of Deviance Table
##
## Model 1: mpg_G ~ cylinders + displacement + horsepower + weight + year_70 +
## origin
## Model 2: mpg_G ~ cylinders + displacement + horsepower + weight + acceleration +
## year_70 + origin
## Resid. Df Resid. Dev Df Deviance Pr(>Chi)
## 1 384 152.31
## 2 383 152.31 1 0.0081963 0.9279
anova(fit.logit2,fit.logit1, test="LR")
## Analysis of Deviance Table
##
## Model 1: mpg_G ~ displacement + horsepower + weight + year_70 + origin
## Model 2: mpg_G ~ cylinders + displacement + horsepower + weight + year_70 +
## origin
## Resid. Df Resid. Dev Df Deviance Pr(>Chi)
## 1 385 152.68
## 2 384 152.31 1 0.36438 0.5461
anova(fit.logit3,fit.logit2, test="LR")
## Analysis of Deviance Table
##
## Model 1: mpg_G ~ horsepower + weight + year_70 + origin
## Model 2: mpg_G ~ displacement + horsepower + weight + year_70 + origin
## Resid. Df Resid. Dev Df Deviance Pr(>Chi)
## 1 386 153.73
## 2 385 152.68 1 1.0515 0.3052
anova(fit.logit4,fit.logit3, test="LR")
## Analysis of Deviance Table
##
## Model 1: mpg_G ~ horsepower + weight + year_70
## Model 2: mpg_G ~ horsepower + weight + year_70 + origin
## Resid. Df Resid. Dev Df Deviance Pr(>Chi)
## 1 388 160.58
## 2 386 153.73 2 6.8528 0.0325 *
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
\[\begin{align} &log(\frac{P(Y=1)}{(1-P(Y=1))})=13.796380-0.042209*horsepower-0.004607*weight+0.457663*year_{70} \\ &log(\frac{P(Y=1)}{(1-P(Y=1))})=13.796380-0.042209*horsepower-0.004607*weight+0.457663*year_{70}+1.335225*origin2 \\ &log(\frac{P(Y=1)}{(1-P(Y=1))})=13.796380-0.042209*horsepower-0.004607*weight+0.457663*year_{70}+0.628677*origin3 \\ \end{align}\]fit.logit3 선택
fit.logit3 에서 horsepower, weight, year_70, origin2 변수가 유의수준 0.05하에 유의하게 나왔으며 확률로 변환 하면 다음과 같이 식이 정리된다.
\[P(Y=1)=\frac{e^{13.796380-0.042209*horsepower-0.004607*weight+0.457663*year_{70}}}{1+e^{13.796380-0.042209*horsepower-0.004607*weight+0.457663*year_{70}}})\] \[해석: \ American에서 \ 제조된 \ 차량의 \ 경우 \ horsepower가 \ 10 \ 증가할 \ 때 \ e^{-0.042209*10}=0.656배 \ 정도 \ "mpg가 \ 22.75(median)보다 \ 큰 \ 확률"이 \ 감소된다.\]origin이 American일 경우
\[P(Y=1)=\frac{e^{13.796380-0.042209*horsepower-0.004607*weight+0.457663*year_{70}+1.335225*origin2}}{1+e^{13.796380-0.042209*horsepower-0.004607*weight+0.457663*year_{70}+1.335225*origin2}})\] \[해석: \ European에서 \ 제조된 \ 차량의 \ 경우 \ horsepower가 \ 10 \ 증가할 \ 때 \ e^{-0.042209*10+1.335225}=2.49배 \ 정도 \ "mpg가 \ 22.75(median)보다 \ 큰 \ 확률"이 \ 증가된다.\]origin이 European일 경우
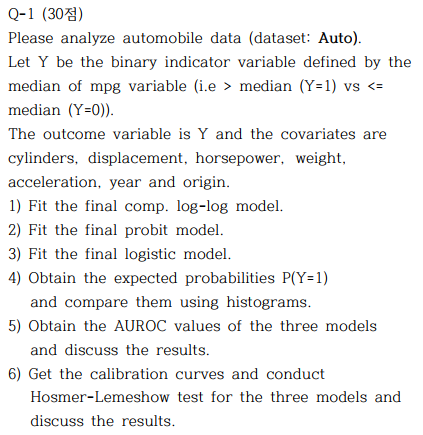
Q-1 4)
par(mfrow = c(3, 2))
hist(fitted(fit.cloglog), col="coral")
hist(fitted(fit.cloglog1), col="coral1")
hist(fitted(fit.cloglog2), col="coral2")
hist(fitted(fit.cloglog3), col="coral3")
hist(fitted(fit.cloglog4), col="coral4")
par(mfrow = c(3, 2))
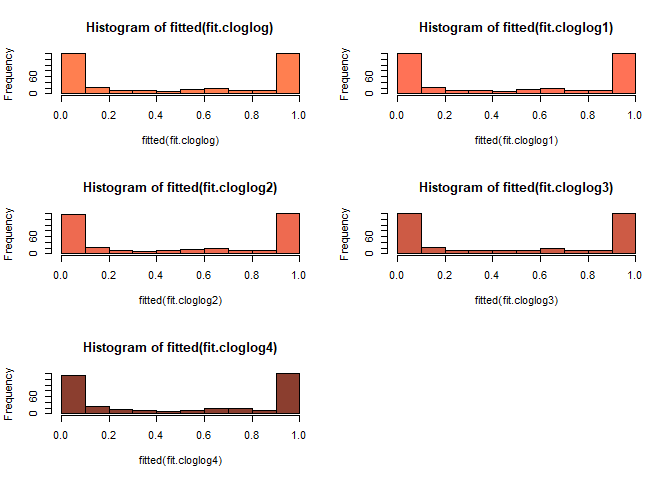
hist(fitted(fit.probit), col="aquamarine")
hist(fitted(fit.probit1), col="aquamarine1")
hist(fitted(fit.probit2), col="aquamarine2")
hist(fitted(fit.probit3), col="aquamarine3")
hist(fitted(fit.probit4), col="aquamarine4")
par(mfrow = c(3, 2))
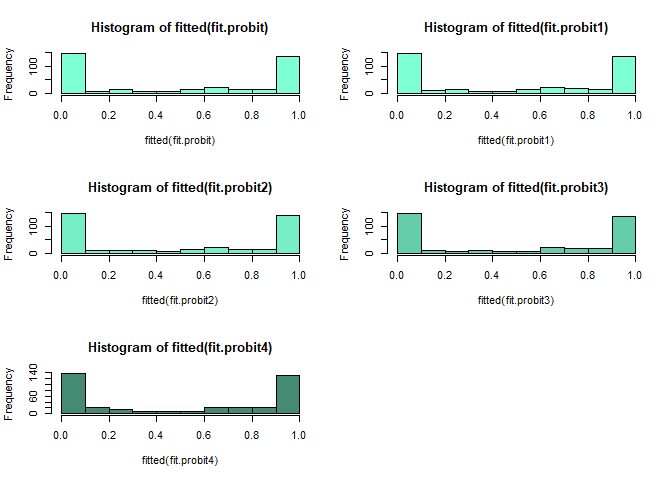
hist(fitted(fit.logit), col="bisque")
hist(fitted(fit.logit1), col="bisque1")
hist(fitted(fit.logit2), col="bisque2")
hist(fitted(fit.logit3), col="bisque3")
hist(fitted(fit.logit4), col="bisque4")
par(mfrow = c(2, 2))
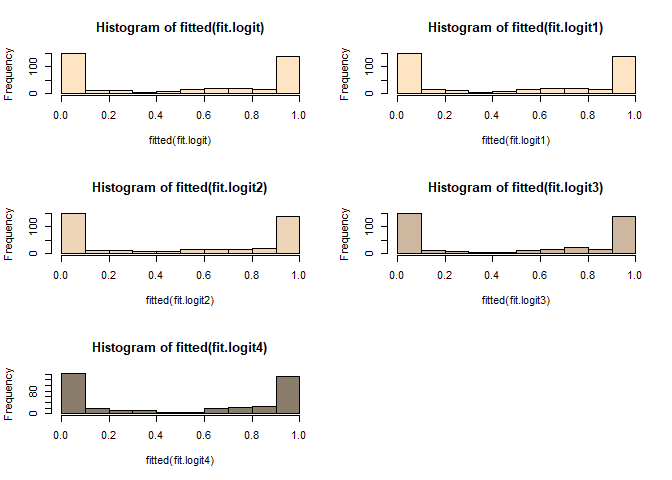
hist(fitted(fit.cloglog3), col="coral3")
hist(fitted(fit.probit4), col="aquamarine4")
hist(fitted(fit.logit3), col="bisque3")
par(mfrow = c(1, 1))
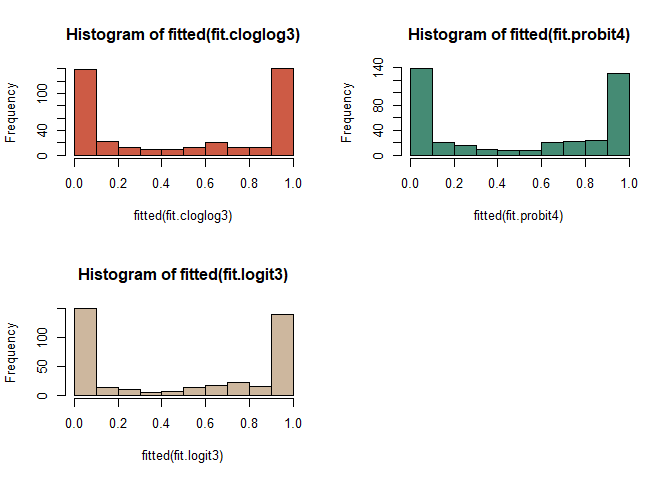
cloglog model이 probit model과 logistic model에 비하여 0부근에서 천천히 빈도가 천천히 내려가고 1에서 급격히 올라가는 것을 볼 수 있다.
probit model은 logistic model 보다 1에 천천히 올라가다가 어느 순간 급격히 올라가는 양상을 볼 수 있다.
Q-1 5)
library(ROCR)
pred1 <- prediction(fitted(fit.cloglog3), mpg_G)
perf1 <- performance(pred1,"tpr","fpr")
performance(pred1,"auc")@y.values
## [[1]]
## [1] 0.9750625
pred2 <- prediction(fitted(fit.probit4), mpg_G)
perf2 <- performance(pred2,"tpr","fpr")
performance(pred2,"auc")@y.values
## [[1]]
## [1] 0.9749584
pred3 <- prediction(fitted(fit.logit3), mpg_G)
perf3 <- performance(pred3,"tpr","fpr")
performance(pred3,"auc")@y.values
## [[1]]
## [1] 0.9753488
par(mfrow = c(1, 3))
plot(perf1,col="coral")
title(main= list("fit.cloglog3", cex= 1.5, col = "coral",font = 3))
legend("bottomright",bty='n', lty=c(1,3,5), c('auc=0.9750625'))
plot(perf2,col="coral")
title(main= list("fit.probit4", cex= 1.5, col = "coral",font = 3))
legend("bottomright",bty='n', lty=c(1,3,5), c('auc=0.9749584'))
plot(perf3,col="coral")
title(main= list("fit.logit3", cex= 1.5, col = "coral",font = 3))
legend("bottomright",bty='n', lty=c(1,3,5), c('auc=0.9753488'))
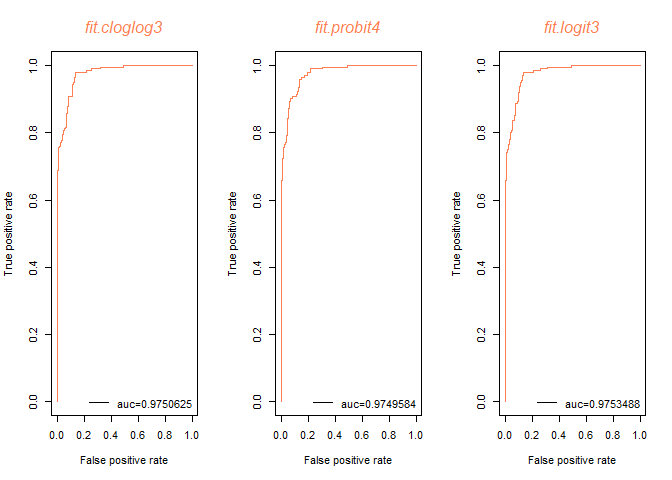
logistic model이 auc값이 가장 크게 나왔다.
fit.logit3 모델을 최종적으로 선택하겠다.
Q-1 6)
#install.packages("glmtoolbox")
library(glmtoolbox)
hltest(fit.cloglog3)
##
## The Hosmer-Lemeshow goodness-of-fit test
##
## Group Size Observed Expected
## 1 39 0 0.004217525
## 2 39 0 0.047055663
## 3 39 1 0.657870853
## 4 39 2 3.552956119
## 5 39 15 12.709573296
## 6 39 26 24.723896623
## 7 39 33 34.976651742
## 8 39 39 38.910995555
## 9 37 37 36.999985069
## 10 43 43 43.000000000
##
## Statistic = 2.94341
## degrees of freedom = 8
## p-value = 0.93786
hltest(fit.probit4)
##
## The Hosmer-Lemeshow goodness-of-fit test
##
## Group Size Observed Expected
## 1 39 0 2.066239e-08
## 2 39 0 1.718546e-04
## 3 39 1 2.434111e-01
## 4 39 2 3.665789e+00
## 5 39 15 1.394751e+01
## 6 39 27 2.703779e+01
## 7 39 32 3.398371e+01
## 8 39 39 3.806513e+01
## 9 39 39 3.890003e+01
## 10 39 39 3.899498e+01
## 11 2 2 1.999998e+00
##
## Statistic = 5.28926
## degrees of freedom = 9
## p-value = 0.8084
hltest(fit.logit3)
##
## The Hosmer-Lemeshow goodness-of-fit test
##
## Group Size Observed Expected
## 1 39 0 1.515836e-04
## 2 39 0 4.487758e-03
## 3 39 1 2.241120e-01
## 4 39 2 2.461195e+00
## 5 39 15 1.384785e+01
## 6 39 26 2.707091e+01
## 7 39 33 3.456875e+01
## 8 39 39 3.805589e+01
## 9 39 39 3.880079e+01
## 10 39 39 3.896615e+01
## 11 2 2 1.999719e+00
##
## Statistic = 4.9142
## degrees of freedom = 9
## p-value = 0.84172
library(ggplot2)
par(mfrow = c(1, 3))
midpoint<- hltest(fit.cloglog3)$hm[,3]
Percent <- hltest(fit.cloglog3)$hm[,4]
ggplot() + xlab("Bin Midpoint") +
geom_line(aes(midpoint, Percent),
color = "#F8766D",size=1) +
geom_point(aes(midpoint, Percent),
color = "#F8766D", size = 2) +
geom_line(aes(c(0, 40), c(0, 40)), linetype = 2,
color = 'grey50')+labs(title="fit.cloglog3",
x ="binning ", y = "Percent")
midpoint<- hltest(fit.probit4)$hm[,3]
Percent <- hltest(fit.probit4)$hm[,4]
ggplot() + xlab("Bin Midpoint") +
geom_line(aes(midpoint, Percent),
color = "#F8766D",size=1) +
geom_point(aes(midpoint, Percent),
color = "#F8766D", size = 2) +
geom_line(aes(c(0, 40), c(0, 40)), linetype = 2,
color = 'grey50')+labs(title="fit.probit4",
x ="binning ", y = "Percent")
midpoint<- hltest(fit.logit3)$hm[,3]
Percent <- hltest(fit.logit3)$hm[,4]
ggplot() + xlab("Bin Midpoint") +
geom_line(aes(hltest(fit.logit3)$hm[,3], hltest(fit.logit3)$hm[,4]),
color = "#F8766D",size = 1) +
geom_point(aes(hltest(fit.logit3)$hm[,3], hltest(fit.logit3)$hm[,4]),
color = "#F8766D", size = 2) +
geom_line(aes(c(0, 40), c(0, 40)), linetype = 2,
color = 'grey50')+labs(title="fit.logit3",
x ="binning ", y = "Percent")
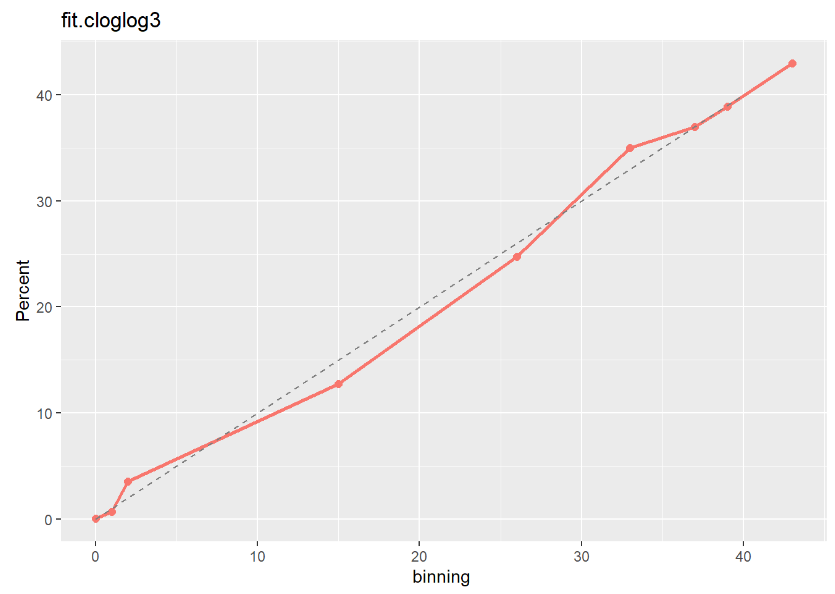
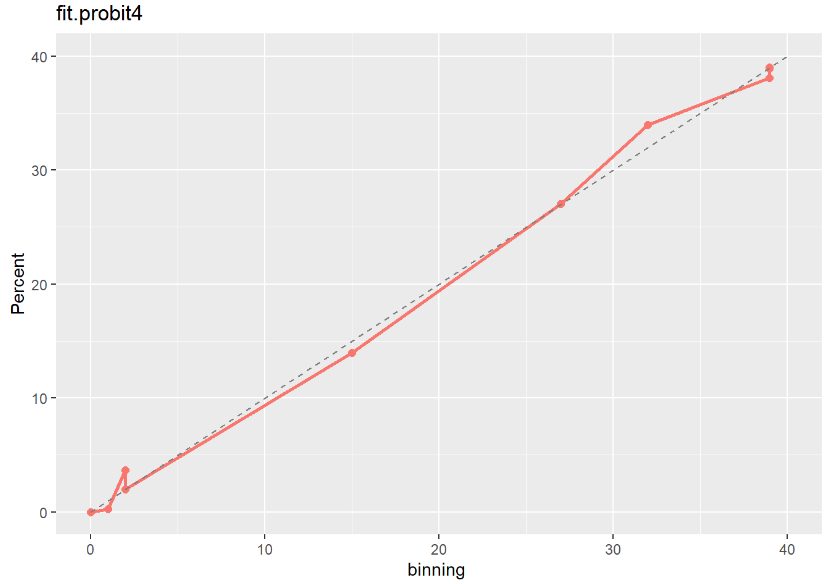
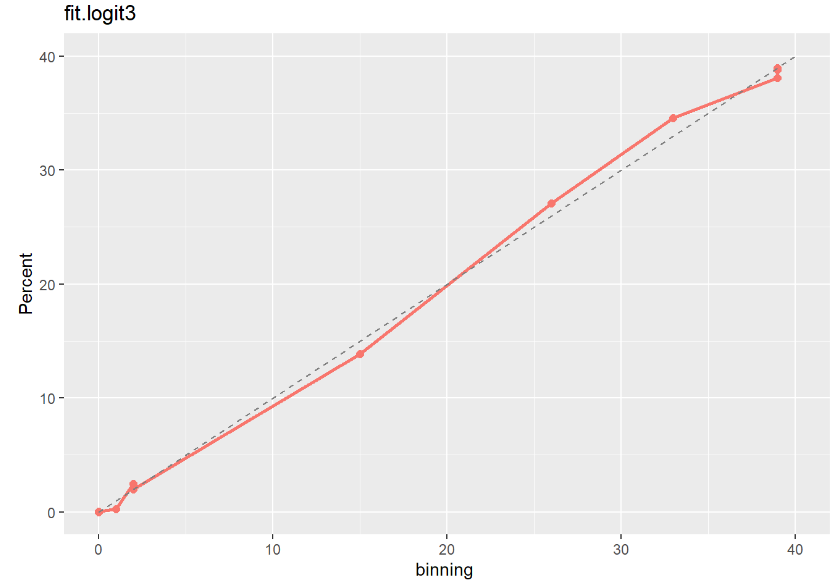
fit.logit3 moodel이 다른 두 모형보다 Calibration Plot 점선에 가깝게 잘 예측된 것으로 보아 최종적으로 fit.logit3 모형을 선택하는 것이 좋아 보인다.
아래는 Calibration Curves plot을 그려주는 패키지이다.
calibration curves 그려주는 함수
#install.packages("predtools")
library(predtools)
par(mfrow = c(3, 2))
auto1$pred1 <- fitted(fit.cloglog3)
auto1$pred2 <- fitted(fit.probit4)
auto1$pred3 <- fitted(fit.logit3)
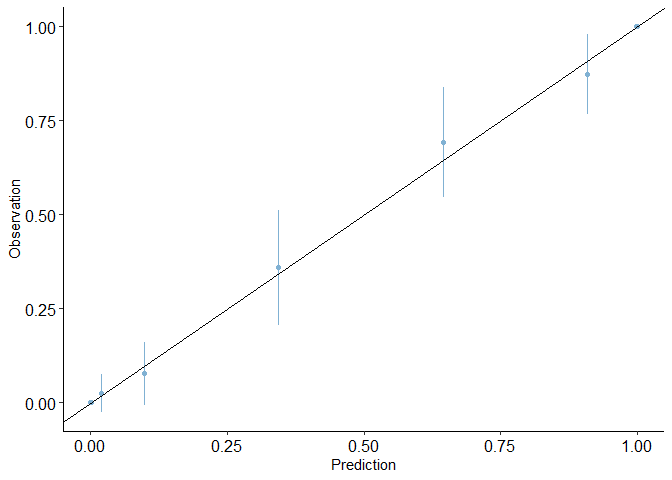
calibration_plot(auto1, obs = "mpg_G", pred = "pred1")
## $calibration_plot
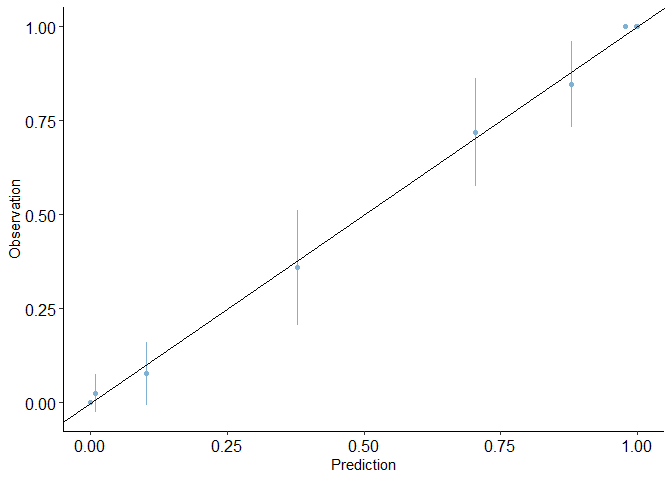
calibration_plot(auto1, obs = "mpg_G", pred = "pred2")
## $calibration_plot
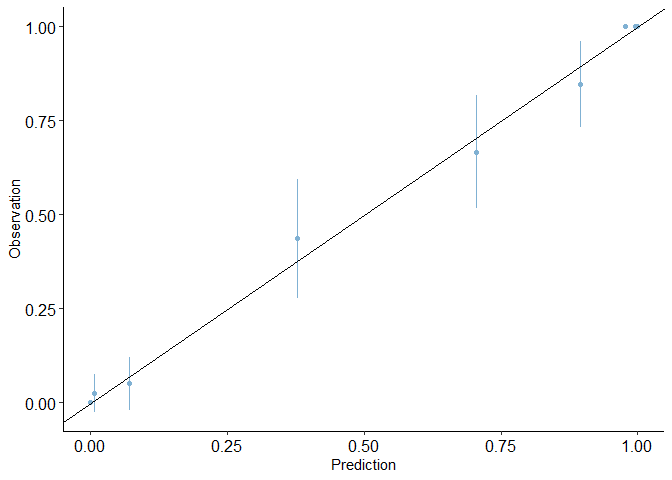
calibration_plot(auto1, obs = "mpg_G", pred = "pred3")
## $calibration_plot
#install.packages("gbm")
library(gbm)
calibrate.plot(auto1$mpg_G,auto1$pred1,line.par = list(col = "black"))
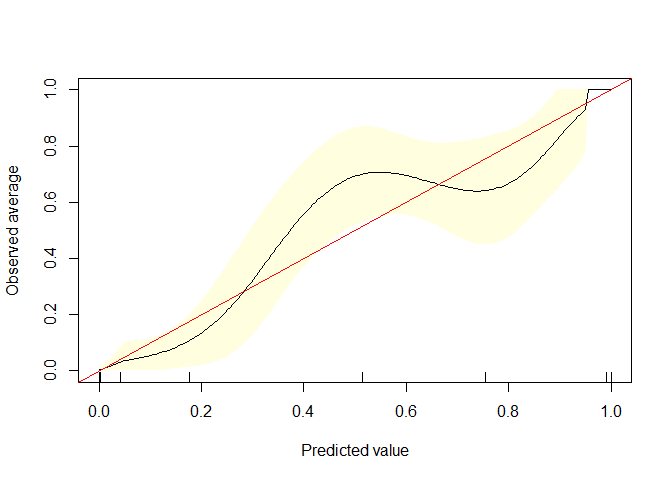
calibrate.plot(auto1$mpg_G,auto1$pred2)
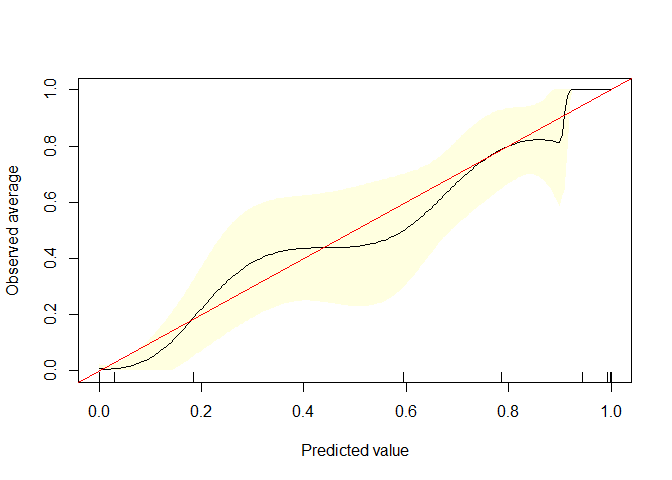
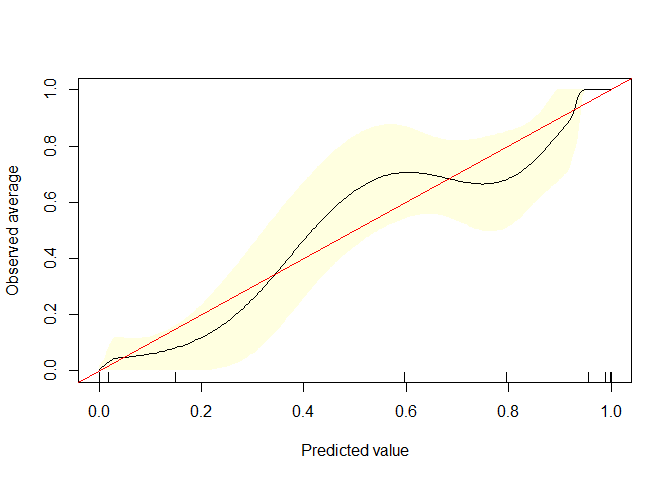
calibrate.plot(auto1$mpg_G,auto1$pred3)
Q-2 )


library(foreign)
esteo <- read.spss('C:/Biostat/Categorical data analysis/Assignment 2/esteo1.sav', to.data.frame=T)
str(esteo)
## 'data.frame': 51 obs. of 12 variables:
## $ id : num 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 ...
## $ bmi : num 24.4 23.7 25.1 20.6 21.8 ...
## $ muscle : num 18 15.8 17.8 14.9 13.9 ...
## $ chid : num 5 2 3 5 4 3 2 3 2 2 ...
## $ menopage: num 46 46 45 50 51 48 44 50 40 45 ...
## $ chol : num 207 178 204 203 164 132 193 264 271 220 ...
## $ cr : num 0.8 0.9 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.6 0.8 0.8 0.8 0.9 ...
## $ alt : num 20 25 37 18 37 10 107 8 14 4 ...
## $ hb : num 12.6 12.3 12.4 12.1 13.6 12.4 13.5 12 14.2 12.4 ...
## $ job : num 2 2 2 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 ...
## $ exer : num 2 2 NA 1 1 1 NA 1 2 1 ...
## $ lscore : num -2.9 -2.9 -2.74 -3.68 -2.97 -3.8 -4.2 -4.14 -3.33 -2.7 ...
## - attr(*, "variable.labels")= Named chr [1:12] "환자번호" "Body Mass Index" "근육강도" "자녀수" ...
## ..- attr(*, "names")= chr [1:12] "id" "bmi" "muscle" "chid" ...
## - attr(*, "codepage")= int 65001
table(is.na(esteo))
##
## FALSE TRUE
## 598 14
esteo1 <- na.omit(esteo)
table(is.na(esteo1))
##
## FALSE
## 468
esteo1$job_G <- as.factor(esteo1$job)
esteo1$exer_G <- as.factor(esteo1$exer)
quantile(esteo1$lscore, probs=0.3)
## 30%
## -3.396
quantile(esteo1$lscore, probs=0.7)
## 70%
## -2.9
esteo1$lscore_G[esteo1$lscore < -3.396]='1'
esteo1$lscore_G[-3.396 <= esteo1$lscore & esteo1$lscore < -2.9]='2'
esteo1$lscore_G[-2.9 <= esteo1$lscore]='3'
library(VGAM)
attach(esteo1)
\[Y=1 \ (lscore<q_{0.7}), \ Y=2 \ (q_{0.3} \leq lscore \leq q_{0.7}), \ Y=3 \ ( lscore \geq q_{0.7})\]우선 데이터를 확인하여 결측치를 제거하여 주고 “나이를 보정한 골밀도” 변수를 30% 백분위수와 70% 백분위수에 대응되는 값을 기준으로 범주형 변수를 생성하였다.
Y=3을 reference로 두었다.
table(esteo1$lscore_G)
##
## 1 2 3
## 12 10 17
Y=3 수가 가장 많은 것은 염두하여두자
이전과 마찬가지로 풀모델에서 각 변수마다 Coefficients를 확인하여 p-value가 가장 큰 값부터 하나씩 제거하여 model을 생성하겠다.
fit <- vglm(lscore_G ~ bmi + muscle + chid + menopage + chol + cr + alt + hb + job_G + exer_G, family = multinomial (refLevel="3"))
summary(fit)@ coef3
## Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
## (Intercept):1 303.32947507 217.14718463 1.39688422 0.1624484
## (Intercept):2 -36.26701041 18.36957529 -1.97429771 0.0483479
## bmi:1 -1.46421242 1.09683738 -1.33494031 0.1818959
## bmi:2 0.12630742 0.30656854 0.41200385 0.6803366
## muscle:1 0.51211360 0.48200617 1.06246275 0.2880257
## muscle:2 -0.12415625 0.18392377 -0.67504190 0.4996491
## chid:1 -0.95082194 1.01587634 -0.93596229 0.3492926
## chid:2 -0.33293721 0.42730221 -0.77916098 0.4358849
## menopage:1 -2.47401245 1.81887302 -1.36018976 0.1737699
## menopage:2 0.29945724 0.19411029 1.54271696 0.1228995
## chol:1 0.04549101 0.04670153 0.97407964 0.3300170
## chol:2 -0.01326953 0.01594567 -0.83217111 0.4053124
## cr:1 -69.33510499 45.16049731 -1.53530428 0.1247091
## cr:2 7.39243139 5.95714632 1.24093500 0.2146298
## alt:1 -0.42206264 0.28232250 -1.49496635 0.1349232
## alt:2 0.07945043 0.07365748 1.07864719 0.2807450
## hb:1 -8.60408312 6.48210196 -1.32736004 0.1843896
## hb:2 1.07885578 0.69817798 1.54524464 0.1222871
## job_G2:1 -5.33068839 4.74350709 -1.12378632 0.2611037
## job_G2:2 3.09178468 2.09124336 1.47844327 0.1392892
## exer_G2:1 1.52565701 2.16803408 0.70370527 0.4816163
## exer_G2:2 0.08451425 1.33627256 0.06324626 0.9495704
#exer제거 모형
fit2 <- vglm(lscore_G ~ bmi + muscle + chid + menopage + chol + cr + alt + hb + job_G, family = multinomial (refLevel="3"))
summary(fit2)@ coef3
## Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
## (Intercept):1 304.39419534 216.75294271 1.4043371 0.16021850
## (Intercept):2 -36.28806899 18.14936736 -1.9994123 0.04556376
## bmi:1 -1.48099240 1.10113495 -1.3449690 0.17863524
## bmi:2 0.13505871 0.30627444 0.4409728 0.65923266
## muscle:1 0.49961539 0.44815711 1.1148220 0.26492673
## muscle:2 -0.12431353 0.18525427 -0.6710427 0.50219331
## chid:1 -0.89699816 0.93904263 -0.9552262 0.33946330
## chid:2 -0.32825680 0.41712099 -0.7869582 0.43130632
## menopage:1 -2.54813351 1.89339534 -1.3458011 0.17836667
## menopage:2 0.29460556 0.17928293 1.6432438 0.10033250
## chol:1 0.04996175 0.04856642 1.0287304 0.30360639
## chol:2 -0.01333918 0.01584320 -0.8419498 0.39981604
## cr:1 -68.68473566 44.30558078 -1.5502502 0.12108147
## cr:2 7.48479392 5.89069230 1.2706136 0.20386614
## alt:1 -0.41037402 0.27099156 -1.5143424 0.12993901
## alt:2 0.07727296 0.07117550 1.0856679 0.27762593
## hb:1 -8.49903544 6.27565440 -1.3542867 0.17564492
## hb:2 1.08369883 0.69921497 1.5498793 0.12117048
## job_G2:1 -5.12972051 4.23195531 -1.2121396 0.22545896
## job_G2:2 3.09736706 2.07164973 1.4951210 0.13488286
#bmi제거 모형
fit3 <- vglm(lscore_G ~ muscle + chid + menopage + chol + cr + alt + hb + job_G, family = multinomial (refLevel="3"))
summary(fit3)@ coef3
## Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
## (Intercept):1 66.533259048 31.92176565 2.08425999 0.03713652
## (Intercept):2 -34.721952644 17.61562120 -1.97108874 0.04871373
## muscle:1 -0.084953305 0.16946974 -0.50128893 0.61616779
## muscle:2 -0.087473185 0.16242601 -0.53854173 0.59020310
## chid:1 0.031767313 0.39287526 0.08085852 0.93555446
## chid:2 -0.323450455 0.43359039 -0.74598160 0.45567853
## menopage:1 -0.551912273 0.28154090 -1.96032715 0.04995756
## menopage:2 0.308460699 0.18671623 1.65202939 0.09852856
## chol:1 0.005244027 0.01851826 0.28318138 0.77703780
## chol:2 -0.014317898 0.01571799 -0.91092414 0.36233534
## cr:1 -17.315599222 10.52104067 -1.64580670 0.09980356
## cr:2 7.459370301 6.05491069 1.23195381 0.21796634
## alt:1 -0.182618268 0.08469702 -2.15613563 0.03107308
## alt:2 0.084734052 0.07019155 1.20718311 0.22736163
## hb:1 -1.939732997 1.21225273 -1.60010611 0.10957505
## hb:2 1.097260725 0.69659805 1.57517054 0.11521709
## job_G2:1 -0.508037988 1.42432385 -0.35668713 0.72132604
## job_G2:2 3.220926291 2.13625193 1.50774647 0.13161943
#chid제거 모형
fit4 <- vglm(lscore_G ~ muscle + menopage + chol + cr + alt + hb + job_G, family = multinomial (refLevel="3"))
summary(fit4)@ coef3
## Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
## (Intercept):1 66.861623425 31.64274364 2.1130160 0.03459940
## (Intercept):2 -31.680252356 16.87836966 -1.8769735 0.06052173
## muscle:1 -0.092722961 0.16798136 -0.5519836 0.58095957
## muscle:2 -0.084458718 0.15753292 -0.5361338 0.59186611
## menopage:1 -0.553461560 0.27836926 -1.9882280 0.04678648
## menopage:2 0.245517784 0.15984048 1.5360175 0.12453408
## chol:1 0.004142469 0.01792600 0.2310872 0.81724703
## chol:2 -0.012450128 0.01573704 -0.7911353 0.42886507
## cr:1 -17.600300029 10.45254543 -1.6838291 0.09221470
## cr:2 5.372352091 4.61575080 1.1639173 0.24445754
## alt:1 -0.184158919 0.08460030 -2.1768116 0.02949463
## alt:2 0.085575773 0.07055039 1.2129739 0.22513982
## hb:1 -1.905176524 1.18869810 -1.6027421 0.10899160
## hb:2 1.085007473 0.70770287 1.5331398 0.12524140
## job_G2:1 -0.466099203 1.41659931 -0.3290268 0.74213540
## job_G2:2 3.389538791 2.26216042 1.4983636 0.13403881
#chol제거 모형
fit5 <- vglm(lscore_G ~ muscle + menopage + cr + alt + hb + job_G, family = multinomial (refLevel="3"))
summary(fit5)@ coef3
## Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
## (Intercept):1 63.84258488 29.51978297 2.1627051 0.03056387
## (Intercept):2 -28.47736073 14.76561204 -1.9286272 0.05377716
## muscle:1 -0.09273250 0.16603985 -0.5584955 0.57650609
## muscle:2 -0.11302966 0.15309238 -0.7383101 0.46032602
## menopage:1 -0.53309790 0.26721006 -1.9950518 0.04603723
## menopage:2 0.21490340 0.14374029 1.4950811 0.13489328
## cr:1 -16.33723053 9.55153415 -1.7104300 0.08718639
## cr:2 5.18409680 4.48772702 1.1551720 0.24801998
## alt:1 -0.18105007 0.08320399 -2.1759783 0.02955689
## alt:2 0.08355327 0.06549708 1.2756794 0.20206886
## hb:1 -1.75418156 1.04051963 -1.6858707 0.09182071
## hb:2 0.85075490 0.61526311 1.3827497 0.16674162
## job_G2:1 -0.42836989 1.40605655 -0.3046605 0.76062474
## job_G2:2 2.66045124 1.79079403 1.4856266 0.13737792
#job제거 모형
fit6 <- vglm(lscore_G ~ muscle + menopage + cr + alt + hb, family = multinomial (refLevel="3"))
summary(fit6)@ coef3
## Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
## (Intercept):1 60.44882635 26.91284214 2.2460960 0.02469786
## (Intercept):2 -17.41490244 10.77699211 -1.6159335 0.10610869
## muscle:1 -0.11549875 0.16065019 -0.7189457 0.47217440
## muscle:2 -0.09718848 0.14491072 -0.6706783 0.50242546
## menopage:1 -0.51388858 0.25644563 -2.0038890 0.04508195
## menopage:2 0.14280272 0.11817492 1.2084012 0.22689298
## cr:1 -15.13999937 8.77327213 -1.7256959 0.08440214
## cr:2 3.82562643 3.21391622 1.1903317 0.23391604
## alt:1 -0.17659748 0.07611242 -2.3202188 0.02032904
## alt:2 0.03534878 0.05184952 0.6817570 0.49539260
## hb:1 -1.62798789 0.94648586 -1.7200340 0.08542626
## hb:2 0.58098736 0.59108221 0.9829214 0.32564612
#muscle제거 모형
fit7 <- vglm(lscore_G ~ menopage + cr + alt + hb, family = multinomial (refLevel="3"))
summary(fit7)@ coef3
## Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
## (Intercept):1 64.68754135 26.41186863 2.4491846 0.01431801
## (Intercept):2 -18.17073229 10.92823323 -1.6627328 0.09636593
## menopage:1 -0.52478090 0.25257072 -2.0777583 0.03773163
## menopage:2 0.16327536 0.11487536 1.4213261 0.15522197
## cr:1 -15.91666067 8.55653714 -1.8601755 0.06286070
## cr:2 4.17015616 3.51895689 1.1850546 0.23599585
## alt:1 -0.18742414 0.07673327 -2.4425409 0.01458428
## alt:2 0.04061331 0.05273348 0.7701617 0.44120400
## hb:1 -2.01135160 0.81279011 -2.4746261 0.01333757
## hb:2 0.40804284 0.52944181 0.7707039 0.44088249
#alt제거 모형
fit8 <- vglm(lscore_G ~ menopage + cr + hb, family = multinomial (refLevel="3"))
summary(fit8)@ coef3
## Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
## (Intercept):1 27.1284315 12.0530504 2.2507523 0.02440123
## (Intercept):2 -20.1795406 11.8121090 -1.7083774 0.08756633
## menopage:1 -0.1936631 0.1290587 -1.5005817 0.13346379
## menopage:2 0.1754191 0.1138383 1.5409501 0.12332893
## cr:1 -6.1157035 3.8709605 -1.5798930 0.11413137
## cr:2 4.1965834 3.5895046 1.1691261 0.24235284
## hb:1 -1.1122904 0.5353496 -2.0776897 0.03773795
## hb:2 0.5946488 0.5984590 0.9936334 0.32040140
#hb제거 모형
fit9 <- vglm(lscore_G ~ menopage + cr, family = multinomial (refLevel="3"))
summary(fit9)@ coef3
## Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
## (Intercept):1 7.64222292 6.7847001 1.1263907 0.26000019
## (Intercept):2 -11.16398607 6.5325727 -1.7089724 0.08745607
## menopage:1 -0.08552023 0.1046863 -0.8169193 0.41397454
## menopage:2 0.16779758 0.1186633 1.4140647 0.15734292
## cr:1 -5.33981691 4.0988608 -1.3027563 0.19265796
## cr:2 2.93260416 3.1110380 0.9426449 0.34586255
#menopage제거 모형
fit10 <- vglm(lscore_G ~ cr, family = multinomial (refLevel="3"))
summary(fit10)@ coef3
## Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
## (Intercept):1 2.525091 2.398367 1.052837 0.2924155
## (Intercept):2 -2.700562 1.993888 -1.354421 0.1756022
## cr:1 -3.941953 3.239308 -1.216912 0.2236377
## cr:2 2.645765 2.453279 1.078461 0.2808282
fit0 <- vglm(lscore_G ~ 1, family=multinomial)
summary(fit0)
##
## Call:
## vglm(formula = lscore_G ~ 1, family = multinomial)
##
## Coefficients:
## Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
## (Intercept):1 -0.3483 0.3770 -0.924 0.356
## (Intercept):2 -0.5306 0.3985 -1.331 0.183
##
## Names of linear predictors: log(mu[,1]/mu[,3]), log(mu[,2]/mu[,3])
##
## Residual deviance: 83.7391 on 76 degrees of freedom
##
## Log-likelihood: -41.8695 on 76 degrees of freedom
##
## Number of Fisher scoring iterations: 3
##
## No Hauck-Donner effect found in any of the estimates
##
##
## Reference group is level 3 of the response
deviance(fit0)
## [1] 83.73909
deviance(fit0)-deviance(fit)
## [1] 50.15896
lrtest(fit0,fit)
## Likelihood ratio test
##
## Model 1: lscore_G ~ 1
## Model 2: lscore_G ~ bmi + muscle + chid + menopage + chol + cr + alt +
## hb + job_G + exer_G
## #Df LogLik Df Chisq Pr(>Chisq)
## 1 76 -41.87
## 2 56 -16.79 -20 50.159 0.0002102 ***
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
deviance(fit2)-deviance(fit)
## [1] 0.5013088
lrtest(fit2,fit)
## Likelihood ratio test
##
## Model 1: lscore_G ~ bmi + muscle + chid + menopage + chol + cr + alt +
## hb + job_G
## Model 2: lscore_G ~ bmi + muscle + chid + menopage + chol + cr + alt +
## hb + job_G + exer_G
## #Df LogLik Df Chisq Pr(>Chisq)
## 1 58 -17.041
## 2 56 -16.790 -2 0.5013 0.7783
deviance(fit3)-deviance(fit2)
## [1] 11.58745
lrtest(fit3,fit2)
## Likelihood ratio test
##
## Model 1: lscore_G ~ muscle + chid + menopage + chol + cr + alt + hb +
## job_G
## Model 2: lscore_G ~ bmi + muscle + chid + menopage + chol + cr + alt +
## hb + job_G
## #Df LogLik Df Chisq Pr(>Chisq)
## 1 60 -22.834
## 2 58 -17.041 -2 11.587 0.003047 **
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
deviance(fit4)-deviance(fit2)
## [1] 12.25574
lrtest(fit4,fit2)
## Likelihood ratio test
##
## Model 1: lscore_G ~ muscle + menopage + chol + cr + alt + hb + job_G
## Model 2: lscore_G ~ bmi + muscle + chid + menopage + chol + cr + alt +
## hb + job_G
## #Df LogLik Df Chisq Pr(>Chisq)
## 1 62 -23.169
## 2 58 -17.041 -4 12.256 0.01555 *
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
deviance(fit5)-deviance(fit2)
## [1] 13.09465
lrtest(fit5,fit2)
## Likelihood ratio test
##
## Model 1: lscore_G ~ muscle + menopage + cr + alt + hb + job_G
## Model 2: lscore_G ~ bmi + muscle + chid + menopage + chol + cr + alt +
## hb + job_G
## #Df LogLik Df Chisq Pr(>Chisq)
## 1 64 -23.588
## 2 58 -17.041 -6 13.095 0.04156 *
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
deviance(fit6)-deviance(fit2)
## [1] 16.60859
lrtest(fit6,fit2)
## Likelihood ratio test
##
## Model 1: lscore_G ~ muscle + menopage + cr + alt + hb
## Model 2: lscore_G ~ bmi + muscle + chid + menopage + chol + cr + alt +
## hb + job_G
## #Df LogLik Df Chisq Pr(>Chisq)
## 1 66 -25.345
## 2 58 -17.041 -8 16.609 0.03445 *
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
deviance(fit7)-deviance(fit2)
## [1] 17.43941
lrtest(fit7,fit2)
## Likelihood ratio test
##
## Model 1: lscore_G ~ menopage + cr + alt + hb
## Model 2: lscore_G ~ bmi + muscle + chid + menopage + chol + cr + alt +
## hb + job_G
## #Df LogLik Df Chisq Pr(>Chisq)
## 1 68 -25.760
## 2 58 -17.041 -10 17.439 0.06519 .
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
deviance(fit8)-deviance(fit7)
## [1] 12.20311
lrtest(fit8,fit7)
## Likelihood ratio test
##
## Model 1: lscore_G ~ menopage + cr + hb
## Model 2: lscore_G ~ menopage + cr + alt + hb
## #Df LogLik Df Chisq Pr(>Chisq)
## 1 70 -31.862
## 2 68 -25.760 -2 12.203 0.002239 **
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
deviance(fit9)-deviance(fit7)
## [1] 21.61579
lrtest(fit9,fit7)
## Likelihood ratio test
##
## Model 1: lscore_G ~ menopage + cr
## Model 2: lscore_G ~ menopage + cr + alt + hb
## #Df LogLik Df Chisq Pr(>Chisq)
## 1 72 -36.568
## 2 68 -25.760 -4 21.616 0.000239 ***
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
deviance(fit10)-deviance(fit7)
## [1] 25.89105
lrtest(fit10,fit7)
## Likelihood ratio test
##
## Model 1: lscore_G ~ cr
## Model 2: lscore_G ~ menopage + cr + alt + hb
## #Df LogLik Df Chisq Pr(>Chisq)
## 1 74 -38.706
## 2 68 -25.760 -6 25.891 0.0002333 ***
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
모형 fit7 선택
fit7 모형
summary(fit7)@ coef3
## Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
## (Intercept):1 64.68754135 26.41186863 2.4491846 0.01431801
## (Intercept):2 -18.17073229 10.92823323 -1.6627328 0.09636593
## menopage:1 -0.52478090 0.25257072 -2.0777583 0.03773163
## menopage:2 0.16327536 0.11487536 1.4213261 0.15522197
## cr:1 -15.91666067 8.55653714 -1.8601755 0.06286070
## cr:2 4.17015616 3.51895689 1.1850546 0.23599585
## alt:1 -0.18742414 0.07673327 -2.4425409 0.01458428
## alt:2 0.04061331 0.05273348 0.7701617 0.44120400
## hb:1 -2.01135160 0.81279011 -2.4746261 0.01333757
## hb:2 0.40804284 0.52944181 0.7707039 0.44088249
\[\begin{align} \hat{\pi_1}=\frac{e^{64.68754135-0.52478090*menopage-15.91666067*cr-0.18742414*alt-2.01135160*hb}}{1+e^{64.68754135-0.52478090*menopage-15.91666067*cr-0.18742414*alt-2.01135160*hb}+e^{-18.17073229+0.16327536*menopage+4.17015616*cr+0.04061331*alt+0.40804284*hb}} \\ \hat{\pi_2}=\frac{e^{-18.17073229+0.16327536*menopage+4.17015616*cr+0.04061331*alt+0.40804284*hb}}{1+e^{64.68754135-0.52478090*menopage-15.91666067*cr-0.18742414*alt-2.01135160*hb}+e^{-18.17073229+0.16327536*menopage+4.17015616*cr+0.04061331*alt+0.40804284*hb}} \\ \hat{\pi_3}= \frac{1}{1+e^{64.68754135-0.52478090*menopage-15.91666067*cr-0.18742414*alt-2.01135160*hb}+e^{-18.17073229+0.16327536*menopage+4.17015616*cr+0.04061331*alt+0.40804284*hb}} \end{align}\] \[\begin{align} & log(\frac{\hat{\pi_1}}{\hat{\pi_3}})=64.68754135-0.52478090*menopage-15.91666067*cr-0.18742414*alt-2.01135160*hb \\ & log(\frac{\hat{\pi_2}}{\hat{\pi_3}})=-18.17073229+0.16327536*menopage+4.17015616*cr+0.04061331*alt+0.40804284*hb \\ & log(\frac{\hat{\pi_1}}{\hat{\pi_2}})=log(\frac{\hat{\pi_1}}{\hat{\pi_3}})-log(\frac{\hat{\pi_2}}{\hat{\pi_3}}) \end{align}\]fit7에서 유의한 변수
menopage “폐경나이”
alt “ALT 수치”
hb “헤모글로빈 수치”
해석: 유의수준 0.05하에 유의한 변수 menopage(폐경나이), alt(ALT 수치), hb(헤모글로빈 수치)를 가지고 세 그룹을 비교하여보자.
수치만으로는 해석하기가 쉽지않다.
왜냐하면 다른 category까지 고려된 coefficient 때문에 우리가 고려하고자 하는 변수가 증가함에 따라 확률이 증가할수도 감소할 수도 있기 때문이다.
그러므로 그래프로 확인하여 보자.
fit7에서 menopage 그래프
#fit7에서 menopage 그래프
summary(esteo1$menopage)
## Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
## 37.00 46.00 50.00 48.41 50.50 57.00
pi_1 <- exp(64.68754135-0.52478090*(esteo1$menopage)-15.91666067*mean(esteo1$cr)-0.18742414*mean(esteo1$alt)-2.01135160*mean(esteo1$hb))/(1+exp(64.68754135-0.52478090*(esteo1$menopage)-15.91666067*mean(esteo1$cr)-0.18742414*mean(esteo1$alt)-2.01135160*mean(esteo1$hb))+exp(-18.17073229+0.16327536*(esteo1$menopage)+4.17015616*mean(esteo1$cr)+0.04061331*mean(esteo1$alt)+0.40804284*mean(esteo1$hb)))
y <- data.frame(esteo1$menopage,pi_1)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo1$menopage,pi_1)$esteo1.menopage, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo1.menopage,y$pi_1,type='l',xlab="menopage", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(37,57),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=1,lwd=2, col=4)
par(new = T)
pi_2 <- exp(-18.17073229+0.16327536*(esteo1$menopage)+4.17015616*mean(esteo1$cr)+0.04061331*mean(esteo1$alt)+0.40804284*mean(esteo1$hb))/(1+exp(64.68754135-0.52478090*(esteo1$menopage)-15.91666067*mean(esteo1$cr)-0.18742414*mean(esteo1$alt)-2.01135160*mean(esteo1$hb))+exp(-18.17073229+0.16327536*(esteo1$menopage)+4.17015616*mean(esteo1$cr)+0.04061331*mean(esteo1$alt)+0.40804284*mean(esteo1$hb)))
y <- data.frame(esteo1$menopage,pi_2)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo1$menopage,pi_2)$esteo1.menopage, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo1.menopage,y$pi_2,type='l',xlab="menopage", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(37,57),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=3,lwd=2, col=3)
par(new = T)
pi_3 <- 1/(1+exp(64.68754135-0.52478090*(esteo1$menopage)-15.91666067*mean(esteo1$cr)-0.18742414*mean(esteo1$alt)-2.01135160*mean(esteo1$hb))+exp(-18.17073229+0.16327536*(esteo1$menopage)+4.17015616*mean(esteo1$cr)+0.04061331*mean(esteo1$alt)+0.40804284*mean(esteo1$hb)))
y <- data.frame(esteo1$menopage,pi_3)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo1$menopage,pi_3)$esteo1.menopage, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo1.menopage,y$pi_3,type='l',xlab="menopage", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(37,57),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=5,lwd=2, col=6)
par(new = T)
legend("topright",bty='n', lty=c(1,3,5), c('lscore<q(0.3)','q(0.3)<lscore<q(0.7)','q(0.7)<lscore'), col=c(4,3,6))
axis(side=1,at=seq(37,57,by=5))
axis(side=2,at=seq(0,1,by=0.2))
title(main= list("fit7에서 menopage 그래프", cex= 1.5, col = "coral",font = 3))
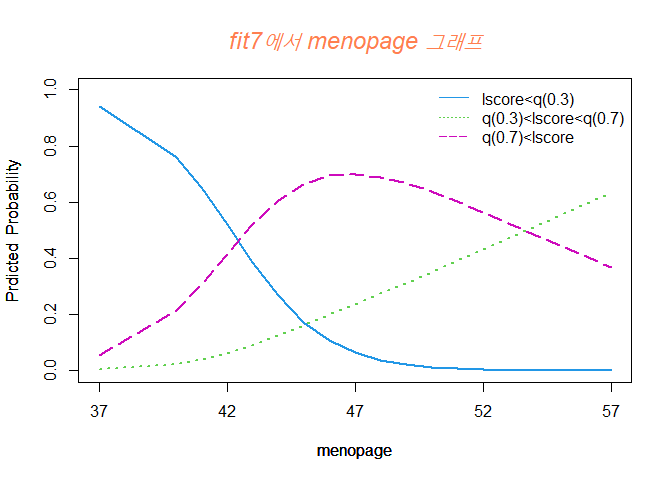
menopage가 증가함에 Y=2 그룹일 확룰이 높아지는 것을 볼 수 있고 Y=1 그룹일 확률은 점점 낮아진다.
또한 Y=3 그룹일 확률은 47세 부근일 때 최대치를 찍고 점점 감소하는 경향을 보인다.
42세까지는 Y=1 그룹일 확률이 제일 높고, 42세부터 52세 정도까지는 Y=3 그룹일 확률이 제일 높으며, 50세 중반 정도부턴 Y=2 그룹일 확률이 높아진다.
fit7에서 alt 그래프
#fit7에서 alt 그래프
summary(esteo1$alt)
## Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
## 4.00 13.50 19.00 25.33 24.50 221.00
pi_1 <- exp(64.68754135-0.52478090*mean(esteo1$menopage)-15.91666067*mean(esteo1$cr)-0.18742414*(esteo1$alt)-2.01135160*mean(esteo1$hb))/(1+exp(64.68754135-0.52478090*mean(esteo1$menopage)-15.91666067*mean(esteo1$cr)-0.18742414*(esteo1$alt)-2.01135160*mean(esteo1$hb))+exp(-18.17073229+0.16327536*mean(esteo1$menopage)+4.17015616*mean(esteo1$cr)+0.04061331*(esteo1$alt)+0.40804284*mean(esteo1$hb)))
y <- data.frame(esteo1$alt,pi_1)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo1$alt,pi_1)$esteo1.alt, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo1.alt,y$pi_1,type='l',xlab="alt 수치", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(4,221),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=1,lwd=2, col=4)
par(new = T)
pi_2 <- exp(-18.17073229+0.16327536*mean(esteo1$menopage)+4.17015616*mean(esteo1$cr)+0.04061331*(esteo1$alt)+0.40804284*mean(esteo1$hb))/(1+exp(64.68754135-0.52478090*mean(esteo1$menopage)-15.91666067*mean(esteo1$cr)-0.18742414*(esteo1$alt)-2.01135160*mean(esteo1$hb))+exp(-18.17073229+0.16327536*mean(esteo1$menopage)+4.17015616*mean(esteo1$cr)+0.04061331*(esteo1$alt)+0.40804284*mean(esteo1$hb)))
y <- data.frame(esteo1$alt,pi_2)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo1$alt,pi_2)$esteo1.alt, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo1.alt,y$pi_2,type='l',xlab="alt 수치", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(4,221),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=3,lwd=2, col=3)
par(new = T)
pi_3 <- 1/(1+exp(64.68754135-0.52478090*mean(esteo1$menopage)-15.91666067*mean(esteo1$cr)-0.18742414*(esteo1$alt)-2.01135160*mean(esteo1$hb))+exp(-18.17073229+0.16327536*mean(esteo1$menopage)+4.17015616*mean(esteo1$cr)+0.04061331*(esteo1$alt)+0.40804284*mean(esteo1$hb)))
y <- data.frame(esteo1$alt,pi_3)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo1$alt,pi_3)$esteo1.alt, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo1.alt,y$pi_3,type='l',xlab="alt 수치", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(4,221),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=5,lwd=2, col=6)
par(new = T)
legend("topleft",bty='n', lty=c(1,3,5), c('lscore<q(0.3)','q(0.3)<lscore<q(0.7)','q(0.7)<lscore'), col=c(4,3,6))
axis(side=1,at=seq(4,221,by=10))
axis(side=2,at=seq(0,1,by=0.2))
title(main= list("fit7에서 alt 그래프", cex= 1.5, col = "coral",font = 3))
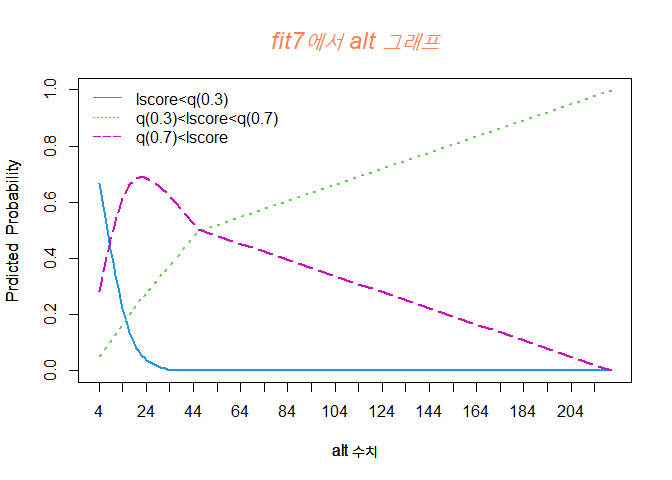
alt 수치가 증가할수록 Y=1 그룹일 확률이 점점 줄어듬을 볼 수 있고, Y=2 그룹일 확률은 점점 증가한다.
또한, Y=3 그룹일 확률은 24세 정도까지 증가하다가 줄어드는 경향을 볼 수 있다.
alt 수치가 4 정도일 때는 Y=1 그룹일 확률이 높고, 4에서 44정도 까지는 Y=3 그룹일 확률이 높으며, 44 이후로는 Y=2 그룹일 확률이 높다.
fit7에서 hb 그래프
#fit7에서 hb 그래프
summary(esteo1$hb)
## Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
## 9.50 12.05 12.60 12.50 13.35 14.20
pi_1 <- exp(64.68754135-0.52478090*mean(esteo1$menopage)-15.91666067*mean(esteo1$cr)-0.18742414*mean(esteo1$alt)-2.01135160*(esteo1$hb))/(1+exp(64.68754135-0.52478090*mean(esteo1$menopage)-15.91666067*mean(esteo1$cr)-0.18742414*mean(esteo1$alt)-2.01135160*(esteo1$hb))+exp(-18.17073229+0.16327536*mean(esteo1$menopage)+4.17015616*mean(esteo1$cr)+0.04061331*mean(esteo1$alt)+0.40804284*(esteo1$hb)))
y <- data.frame(esteo1$hb,pi_1)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo1$hb,pi_1)$esteo1.hb, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo1.hb,y$pi_1,type='l',xlab="hb 수치", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(9.5,14.2),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=1,lwd=2, col=4)
par(new = T)
pi_2 <- exp(-18.17073229+0.16327536*mean(esteo1$menopage)+4.17015616*mean(esteo1$cr)+0.04061331*mean(esteo1$alt)+0.40804284*(esteo1$hb))/(1+exp(64.68754135-0.52478090*mean(esteo1$menopage)-15.91666067*mean(esteo1$cr)-0.18742414*mean(esteo1$alt)-2.01135160*(esteo1$hb))+exp(-18.17073229+0.16327536*mean(esteo1$menopage)+4.17015616*mean(esteo1$cr)+0.04061331*mean(esteo1$alt)+0.40804284*(esteo1$hb)))
y <- data.frame(esteo1$hb,pi_2)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo1$hb,pi_2)$esteo1.hb, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo1.hb,y$pi_2,type='l',xlab="hb 수치", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(9.5,14.2),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=3,lwd=2, col=3)
par(new = T)
pi_3 <- 1/(1+exp(64.68754135-0.52478090*mean(esteo1$menopage)-15.91666067*mean(esteo1$cr)-0.18742414*mean(esteo1$alt)-2.01135160*(esteo1$hb))+exp(-18.17073229+0.16327536*mean(esteo1$menopage)+4.17015616*mean(esteo1$cr)+0.04061331*mean(esteo1$alt)+0.40804284*(esteo1$hb)))
y <- data.frame(esteo1$hb,pi_3)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo1$hb,pi_3)$esteo1.hb, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo1.hb,y$pi_3,type='l',xlab="hb 수치", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(9.5,14.2),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=5,lwd=2, col=6)
par(new = T)
legend("topright",bty='n', lty=c(1,3,5), c('lscore<q(0.3)','q(0.3)<lscore<q(0.7)','q(0.7)<lscore'), col=c(4,3,6))
axis(side=1,at=seq(9.5,14.2,by=0.5))
axis(side=2,at=seq(0,1,by=0.2))
title(main= list("fit7에서 hb 그래프", cex= 1.5, col = "coral",font = 3))
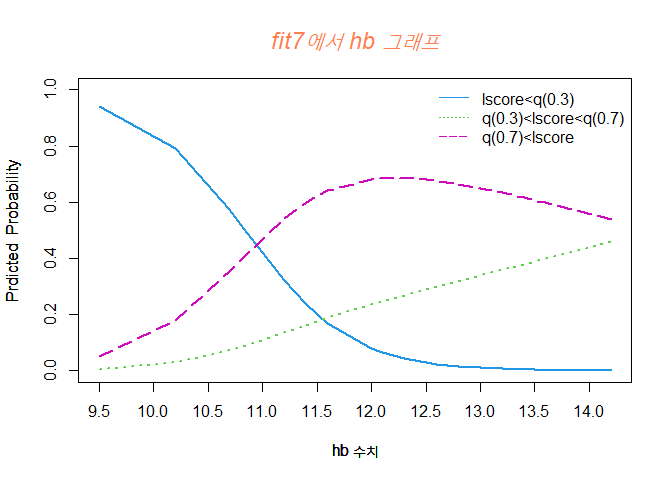
hb 수치가 증가할수록 Y=1 그룹일 확률은 감소하고, Y=2 그룹일 확률은 증가한다.
또한, Y=3 그룹일 확률은 12정도일때까지 증가하고 점점 떨어진다.
hb 수치가 11정도일 때는 Y=1 그룹일 확률이 가장 높으며, 11부터 14까지 Y=3 그룹일 확률이 가장 높다.
hb 수치가 낮을 수록 골밀도 수치가 낮은 그룹일 확률이 높다.
이상치 제거
데이터에서 이상치 때문에 모형에서 유의한 변수가 제거되었을 수도 있으며, 잘못된 coeffcients를 그했을 수도 있으므로 이상치로 판단되는 값을 연구자의 판단에 의하여 구별하고 제거 할지 말지 고려하여 보겠다.
par(mfrow = c(1, 3))
boxplot(esteo1$cr)
legend("topright",bty='n', c('크레아틴닌 수치'))
boxplot(esteo1$hb)
legend("topright",bty='n', c('헤모글로빈 수치'))
boxplot(esteo1$alt)
legend("topright",bty='n', c('ALT 수치'))
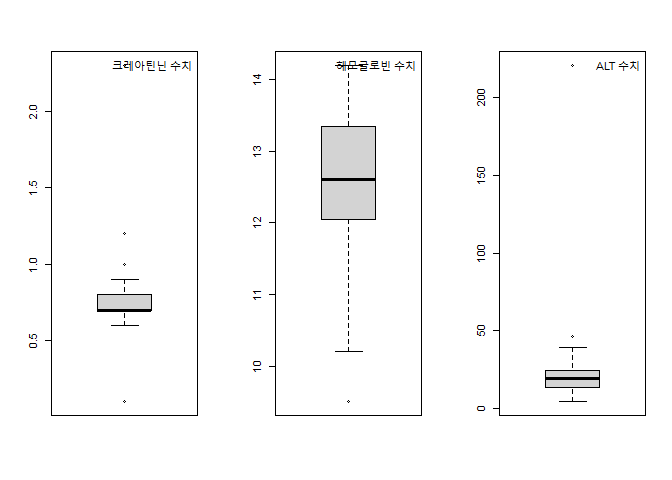
혈중 크레아티닌 농도의 정상범위는 0.50~1.4 mg/dL
빈혈 수치 7~9 g/dL
ALT 정상수치 범위 0~40 IU/L
cr=2.3, 0.1 , alt=221 , hb=9.5 제거하고 다시 데이터를 확인하여 보자.
esteo1$cr2 <- ifelse(esteo1$cr == 2.3 | esteo1$cr == 0.1, NA, esteo1$cr)
esteo1$alt2 <- ifelse(esteo1$alt == 221.00, NA, esteo1$alt)
esteo1$hb2 <- ifelse(esteo1$hb == 9.5, NA, esteo1$hb)
esteo2 <- na.omit(esteo1)
table(is.na(esteo2))
##
## FALSE
## 630
str(esteo2)
## 'data.frame': 35 obs. of 18 variables:
## $ id : num 1 2 4 5 6 8 9 10 11 13 ...
## $ bmi : num 24.4 23.7 20.6 21.8 19.6 ...
## $ muscle : num 18 15.8 14.9 13.9 11.6 ...
## $ chid : num 5 2 5 4 3 3 2 2 2 3 ...
## $ menopage: num 46 46 50 51 48 50 40 45 46 46 ...
## $ chol : num 207 178 203 164 132 264 271 220 210 219 ...
## $ cr : num 0.8 0.9 0.7 0.8 0.6 0.8 0.8 0.9 0.8 0.8 ...
## $ alt : num 20 25 18 37 10 8 14 4 21 19 ...
## $ hb : num 12.6 12.3 12.1 13.6 12.4 12 14.2 12.4 14.1 12.6 ...
## $ job : num 2 2 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 ...
## $ exer : num 2 2 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 2 ...
## $ lscore : num -2.9 -2.9 -3.68 -2.97 -3.8 -4.14 -3.33 -2.7 -3.23 -4 ...
## $ job_G : Factor w/ 2 levels "1","2": 2 2 1 1 2 2 2 2 2 2 ...
## $ exer_G : Factor w/ 2 levels "1","2": 2 2 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 2 ...
## $ lscore_G: chr "3" "3" "1" "2" ...
## $ cr2 : num 0.8 0.9 0.7 0.8 0.6 0.8 0.8 0.9 0.8 0.8 ...
## $ alt2 : num 20 25 18 37 10 8 14 4 21 19 ...
## $ hb2 : num 12.6 12.3 12.1 13.6 12.4 12 14.2 12.4 14.1 12.6 ...
## - attr(*, "variable.labels")= Named chr [1:12] "환자번호" "Body Mass Index" "근육강도" "자녀수" ...
## ..- attr(*, "names")= chr [1:12] "id" "bmi" "muscle" "chid" ...
## - attr(*, "codepage")= int 65001
## - attr(*, "na.action")= 'omit' Named int [1:4] 17 30 31 32
## ..- attr(*, "names")= chr [1:4] "20" "40" "42" "43"
위와 동일하게 풀모델에서 각 변수마다 Coefficients를 확인하여 p-value가 가장 큰 값부터 하나씩 제거하여 model을 생성하겠다.
fit1_1 <- vglm(lscore_G ~ bmi + muscle + chid + menopage + chol + cr + alt + hb + job_G + exer_G, family = multinomial (refLevel="3"), data=esteo2)
summary(fit1_1)@ coef3
## Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
## (Intercept):1 733.90553807 343.87118753 2.13424551 0.03282269
## (Intercept):2 -331.36213075 211.18733223 -1.56904359 0.11663778
## bmi:1 -3.12537399 1.57433781 -1.98519908 0.04712233
## bmi:2 -1.06286291 2.48820462 -0.42716057 0.66926238
## muscle:1 1.19855510 0.64340913 1.86281955 0.06248766
## muscle:2 -1.29775193 2.31560159 -0.56043835 0.57518048
## chid:1 -3.41221181 1.97314828 -1.72932357 0.08375120
## chid:2 0.15449595 5.04109951 0.03064727 0.97555084
## menopage:1 -5.35797722 2.62006253 -2.04498067 0.04085676
## menopage:2 1.37579641 1.58608041 0.86741908 0.38571243
## chol:1 0.09813986 0.06800762 1.44307167 0.14900028
## chol:2 -0.02653841 0.18603262 -0.14265463 0.88656295
## cr:1 -153.25240963 72.56825594 -2.11183813 0.03470034
## cr:2 45.00048055 75.52090512 0.59586787 0.55126350
## alt:1 -0.70636019 0.52563913 -1.34381204 0.17900917
## alt:2 -0.81237074 1.02412901 -0.79323086 0.42764333
## hb:1 -24.87063674 12.02995548 -2.06739225 0.03869721
## hb:2 22.29384591 15.16561737 1.47002561 0.14155482
## job_G2:1 -9.98673062 5.75716042 -1.73466256 0.08280059
## job_G2:2 -0.51407912 13.23942626 -0.03882941 0.96902640
## exer_G2:1 5.55481080 3.72195424 1.49244468 0.13558261
## exer_G2:2 7.79219881 9.83539911 0.79226056 0.42820876
#chid 제거모형
fit1_2 <- vglm(lscore_G ~ bmi + muscle + menopage + chol + cr + alt + hb + job_G + exer_G, family = multinomial (refLevel="3"), data=esteo2)
summary(fit1_2)@ coef3
## Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
## (Intercept):1 353.41090501 2.686902e+02 1.31531016 0.1884057
## (Intercept):2 -813.05638785 2.423180e+03 -0.33553285 0.7372232
## bmi:1 -1.29193457 8.563825e-01 -1.50859527 0.1314022
## bmi:2 -2.10991129 3.731240e+01 -0.05654720 0.9549059
## muscle:1 0.69225802 7.346459e-01 0.94230167 0.3460382
## muscle:2 -3.31556357 2.361340e+01 -0.14041026 0.8883359
## menopage:1 -3.02350047 2.215939e+00 -1.36443313 0.1724313
## menopage:2 3.36229302 1.748244e+01 0.19232399 0.8474884
## chol:1 0.06772898 6.945041e-02 0.97521356 0.3294543
## chol:2 -0.07201443 1.718258e+00 -0.04191131 0.9665694
## cr:1 -84.57611496 6.735595e+01 -1.25565915 0.2092396
## cr:2 108.86906732 5.625420e+02 0.19353054 0.8465435
## alt:1 -0.62978818 5.286018e-01 -1.19142270 0.2334877
## alt:2 -2.01595579 8.627358e+00 -0.23367013 0.8152411
## hb:1 -10.43124178 8.904312e+00 -1.17148208 0.2414051
## hb:2 54.47488651 1.591579e+02 0.34226945 0.7321481
## job_G2:1 -6.24920252 5.525163e+00 -1.13104400 0.2580366
## job_G2:2 -1.45389075 1.100060e+02 -0.01321646 0.9894551
## exer_G2:1 2.22741996 3.619419e+00 0.61540822 0.5382852
## exer_G2:2 18.40378423 9.884008e+01 0.18619758 0.8522898
#job 제거모형
fit1_3 <- vglm(lscore_G ~ bmi + muscle + menopage + chol + cr + alt + hb + exer_G, family = multinomial (refLevel="3"), data=esteo2)
summary(fit1_3)@ coef3
## Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
## (Intercept):1 147.9831899 8.153654e+01 1.81493086 0.06953454
## (Intercept):2 -800.1249801 2.452806e+03 -0.32620805 0.74426695
## bmi:1 -0.6376034 3.656338e-01 -1.74383057 0.08118864
## bmi:2 -2.2167332 3.840239e+01 -0.05772383 0.95396861
## muscle:1 0.1986860 2.832000e-01 0.70157482 0.48294436
## muscle:2 -3.1743461 2.382412e+01 -0.13324084 0.89400292
## menopage:1 -1.2687570 7.214750e-01 -1.75855993 0.07865228
## menopage:2 3.4542785 1.538154e+01 0.22457294 0.82231151
## chol:1 0.0205211 3.118824e-02 0.65797565 0.51055378
## chol:2 -0.0699068 1.486398e+00 -0.04703102 0.96248850
## cr:1 -34.6217724 2.156249e+01 -1.60564795 0.10835128
## cr:2 104.8163906 5.416332e+02 0.19351915 0.84655241
## alt:1 -0.2283863 1.847001e-01 -1.23652530 0.21626337
## alt:2 -1.9025165 7.791353e+00 -0.24418305 0.80708905
## hb:1 -4.2289267 2.761518e+00 -1.53137736 0.12567616
## hb:2 53.1042834 1.646607e+02 0.32250734 0.74706838
## exer_G2:1 0.2810719 2.277786e+00 0.12339699 0.90179274
## exer_G2:2 18.1213036 1.102726e+02 0.16433190 0.86946987
#chol 제거모형
fit1_4 <- vglm(lscore_G ~ bmi + muscle + menopage + cr + alt + hb + exer_G, family = multinomial (refLevel="3"), data=esteo2)
summary(fit1_4)@ coef3
## Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
## (Intercept):1 128.2732089 65.8196346 1.94885933 0.05131223
## (Intercept):2 -752.3948737 1669.0561191 -0.45079064 0.65214045
## bmi:1 -0.6111878 0.3650435 -1.67428772 0.09407407
## bmi:2 -1.7960683 30.2545617 -0.05936521 0.95266122
## muscle:1 0.1481321 0.2148104 0.68959473 0.49044908
## muscle:2 -2.9688886 17.7643892 -0.16712585 0.86727103
## menopage:1 -1.0969087 0.6278621 -1.74705363 0.08062804
## menopage:2 3.4466596 9.8007852 0.35167178 0.72508443
## cr:1 -28.6604342 16.5588859 -1.73081899 0.08348405
## cr:2 90.6336667 359.0126957 0.25245254 0.80069129
## alt:1 -0.1916578 0.1549408 -1.23697440 0.21609659
## alt:2 -1.5159239 4.1179644 -0.36812457 0.71278035
## hb:1 -3.3322698 1.8271158 -1.82378690 0.06818429
## hb:2 47.6103467 107.7467509 0.44187269 0.65858133
## exer_G2:1 0.2017037 2.0005274 0.10082527 0.91968916
## exer_G2:2 18.0414187 74.9138031 0.24082903 0.80968763
#bmi 제거모형
fit1_5 <- vglm(lscore_G ~ muscle + menopage + cr + alt + hb + exer_G, family = multinomial (refLevel="3"), data=esteo2)
summary(fit1_5)@ coef3
## Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
## (Intercept):1 66.57088295 33.8331452 1.9676232 0.04911140
## (Intercept):2 -684.02673778 892.8090232 -0.7661512 0.44358632
## muscle:1 -0.01700698 0.1601329 -0.1062054 0.91541936
## muscle:2 -3.36703004 5.9487909 -0.5660024 0.57139213
## menopage:1 -0.53978967 0.3122776 -1.7285573 0.08388836
## menopage:2 3.14524666 4.8226431 0.6521832 0.51428302
## cr:1 -15.09632079 9.6263012 -1.5682369 0.11682585
## cr:2 71.54149022 150.0435966 0.4768047 0.63350121
## alt:1 -0.14758700 0.1012155 -1.4581460 0.14480031
## alt:2 -1.32953761 3.1300048 -0.4247718 0.67100307
## hb:1 -2.18175766 1.3858636 -1.5742946 0.11541935
## hb:2 41.78536471 58.6241568 0.7127670 0.47598995
## exer_G2:1 -0.39732438 1.4672186 -0.2708011 0.78654404
## exer_G2:2 16.55601220 36.7468936 0.4505418 0.65231981
#muscle 제거모형
fit1_6 <- vglm(lscore_G ~ menopage + cr + alt + hb + exer_G, family = multinomial (refLevel="3"), data=esteo2)
summary(fit1_6)@ coef3
## Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
## (Intercept):1 67.6101584 31.87671441 2.1209889 0.03392273
## (Intercept):2 -230.9476103 131.01616554 -1.7627413 0.07794413
## menopage:1 -0.5430364 0.30440452 -1.7839301 0.07443502
## menopage:2 1.2306747 0.85850610 1.4335073 0.15171292
## cr:1 -15.3195363 9.38328439 -1.6326412 0.10254449
## cr:2 32.6423381 15.65931983 2.0845310 0.03711189
## alt:1 -0.1495793 0.09948299 -1.5035663 0.13269307
## alt:2 -0.2300392 0.18720501 -1.2288089 0.21914346
## hb:1 -2.2575827 1.17344011 -1.9239011 0.05436698
## hb:2 10.9885918 6.12242186 1.7948113 0.07268377
## exer_G2:1 -0.3622089 1.46369124 -0.2474626 0.80455022
## exer_G2:2 7.1585883 5.50524142 1.3003223 0.19349052
#exer 제거모형
fit1_7 <- vglm(lscore_G ~ menopage + cr + alt + hb, family = multinomial (refLevel="3"), data=esteo2)
summary(fit1_7)@ coef3
## Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
## (Intercept):1 71.3128243 28.96237384 2.462258 0.01380655
## (Intercept):2 -129.0950613 68.86079332 -1.874725 0.06083054
## menopage:1 -0.5580365 0.27136261 -2.056424 0.03974171
## menopage:2 0.6856379 0.43781384 1.566049 0.11733718
## cr:1 -15.7973001 8.63210597 -1.830063 0.06724048
## cr:2 22.5497239 11.05605936 2.039581 0.04139212
## alt:1 -0.1529043 0.08751503 -1.747177 0.08060660
## alt:2 -0.2649006 0.16629199 -1.592985 0.11116359
## hb:1 -2.4742042 1.11128758 -2.226430 0.02598538
## hb:2 6.2280412 3.32020126 1.875802 0.06068243
#alt 제거모형
fit1_8 <- vglm(lscore_G ~ menopage + cr + hb, family = multinomial (refLevel="3"), data=esteo2)
summary(fit1_8)@ coef3
## Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
## (Intercept):1 53.4711118 23.1712968 2.307644 0.02101893
## (Intercept):2 -69.2089254 27.7497633 -2.494037 0.01262995
## menopage:1 -0.3046766 0.1651894 -1.844408 0.06512375
## menopage:2 0.3083680 0.1617405 1.906560 0.05657753
## cr:1 -8.8977009 5.8272103 -1.526923 0.12678018
## cr:2 15.4526205 7.3058150 2.115112 0.03442036
## hb:1 -2.6422771 1.1877989 -2.224516 0.02611378
## hb:2 3.1244868 1.3205892 2.365979 0.01798244
deviance(fit1_2)-deviance(fit1_1)
## [1] 9.20352
lrtest(fit1_2,fit1_1)
## Likelihood ratio test
##
## Model 1: lscore_G ~ bmi + muscle + menopage + chol + cr + alt + hb + job_G +
## exer_G
## Model 2: lscore_G ~ bmi + muscle + chid + menopage + chol + cr + alt +
## hb + job_G + exer_G
## #Df LogLik Df Chisq Pr(>Chisq)
## 1 50 -6.1281
## 2 48 -1.5263 -2 9.2035 0.01003 *
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
deviance(fit1_3)-deviance(fit1_1)
## [1] 12.51006
lrtest(fit1_3,fit1_1)
## Likelihood ratio test
##
## Model 1: lscore_G ~ bmi + muscle + menopage + chol + cr + alt + hb + exer_G
## Model 2: lscore_G ~ bmi + muscle + chid + menopage + chol + cr + alt +
## hb + job_G + exer_G
## #Df LogLik Df Chisq Pr(>Chisq)
## 1 52 -7.7814
## 2 48 -1.5263 -4 12.51 0.01394 *
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
deviance(fit1_4)-deviance(fit1_1)
## [1] 12.97605
lrtest(fit1_4,fit1_1)
## Likelihood ratio test
##
## Model 1: lscore_G ~ bmi + muscle + menopage + cr + alt + hb + exer_G
## Model 2: lscore_G ~ bmi + muscle + chid + menopage + chol + cr + alt +
## hb + job_G + exer_G
## #Df LogLik Df Chisq Pr(>Chisq)
## 1 54 -8.0144
## 2 48 -1.5263 -6 12.976 0.04342 *
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
deviance(fit1_5)-deviance(fit1_1)
## [1] 17.76238
lrtest(fit1_5,fit1_1)
## Likelihood ratio test
##
## Model 1: lscore_G ~ muscle + menopage + cr + alt + hb + exer_G
## Model 2: lscore_G ~ bmi + muscle + chid + menopage + chol + cr + alt +
## hb + job_G + exer_G
## #Df LogLik Df Chisq Pr(>Chisq)
## 1 56 -10.4075
## 2 48 -1.5263 -8 17.762 0.02308 *
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
deviance(fit1_6)-deviance(fit1_1)
## [1] 24.743
lrtest(fit1_6,fit1_1)
## Likelihood ratio test
##
## Model 1: lscore_G ~ menopage + cr + alt + hb + exer_G
## Model 2: lscore_G ~ bmi + muscle + chid + menopage + chol + cr + alt +
## hb + job_G + exer_G
## #Df LogLik Df Chisq Pr(>Chisq)
## 1 58 -13.8978
## 2 48 -1.5263 -10 24.743 0.005855 **
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
deviance(fit1_7)-deviance(fit1_1)
## [1] 29.77661
lrtest(fit1_7,fit1_1)
## Likelihood ratio test
##
## Model 1: lscore_G ~ menopage + cr + alt + hb
## Model 2: lscore_G ~ bmi + muscle + chid + menopage + chol + cr + alt +
## hb + job_G + exer_G
## #Df LogLik Df Chisq Pr(>Chisq)
## 1 60 -16.4146
## 2 48 -1.5263 -12 29.777 0.003017 **
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
deviance(fit1_8)-deviance(fit1_1)
## [1] 38.10199
lrtest(fit1_8,fit1_1)
## Likelihood ratio test
##
## Model 1: lscore_G ~ menopage + cr + hb
## Model 2: lscore_G ~ bmi + muscle + chid + menopage + chol + cr + alt +
## hb + job_G + exer_G
## #Df LogLik Df Chisq Pr(>Chisq)
## 1 62 -20.5773
## 2 48 -1.5263 -14 38.102 0.0005013 ***
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
deviance(fit1_2)-deviance(fit1_1)
## [1] 9.20352
lrtest(fit1_2,fit1_1)
## Likelihood ratio test
##
## Model 1: lscore_G ~ bmi + muscle + menopage + chol + cr + alt + hb + job_G +
## exer_G
## Model 2: lscore_G ~ bmi + muscle + chid + menopage + chol + cr + alt +
## hb + job_G + exer_G
## #Df LogLik Df Chisq Pr(>Chisq)
## 1 50 -6.1281
## 2 48 -1.5263 -2 9.2035 0.01003 *
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
deviance(fit1_3)-deviance(fit1_1)
## [1] 12.51006
lrtest(fit1_3,fit1_1)
## Likelihood ratio test
##
## Model 1: lscore_G ~ bmi + muscle + menopage + chol + cr + alt + hb + exer_G
## Model 2: lscore_G ~ bmi + muscle + chid + menopage + chol + cr + alt +
## hb + job_G + exer_G
## #Df LogLik Df Chisq Pr(>Chisq)
## 1 52 -7.7814
## 2 48 -1.5263 -4 12.51 0.01394 *
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
deviance(fit1_4)-deviance(fit1_1)
## [1] 12.97605
lrtest(fit1_4,fit1_1)
## Likelihood ratio test
##
## Model 1: lscore_G ~ bmi + muscle + menopage + cr + alt + hb + exer_G
## Model 2: lscore_G ~ bmi + muscle + chid + menopage + chol + cr + alt +
## hb + job_G + exer_G
## #Df LogLik Df Chisq Pr(>Chisq)
## 1 54 -8.0144
## 2 48 -1.5263 -6 12.976 0.04342 *
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
deviance(fit1_5)-deviance(fit1_1)
## [1] 17.76238
lrtest(fit1_5,fit1_1)
## Likelihood ratio test
##
## Model 1: lscore_G ~ muscle + menopage + cr + alt + hb + exer_G
## Model 2: lscore_G ~ bmi + muscle + chid + menopage + chol + cr + alt +
## hb + job_G + exer_G
## #Df LogLik Df Chisq Pr(>Chisq)
## 1 56 -10.4075
## 2 48 -1.5263 -8 17.762 0.02308 *
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
deviance(fit1_6)-deviance(fit1_1)
## [1] 24.743
lrtest(fit1_6,fit1_1)
## Likelihood ratio test
##
## Model 1: lscore_G ~ menopage + cr + alt + hb + exer_G
## Model 2: lscore_G ~ bmi + muscle + chid + menopage + chol + cr + alt +
## hb + job_G + exer_G
## #Df LogLik Df Chisq Pr(>Chisq)
## 1 58 -13.8978
## 2 48 -1.5263 -10 24.743 0.005855 **
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
deviance(fit1_7)-deviance(fit1_1)
## [1] 29.77661
lrtest(fit1_7,fit1_1)
## Likelihood ratio test
##
## Model 1: lscore_G ~ menopage + cr + alt + hb
## Model 2: lscore_G ~ bmi + muscle + chid + menopage + chol + cr + alt +
## hb + job_G + exer_G
## #Df LogLik Df Chisq Pr(>Chisq)
## 1 60 -16.4146
## 2 48 -1.5263 -12 29.777 0.003017 **
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
deviance(fit1_8)-deviance(fit1_1)
## [1] 38.10199
lrtest(fit1_8,fit1_1)
## Likelihood ratio test
##
## Model 1: lscore_G ~ menopage + cr + hb
## Model 2: lscore_G ~ bmi + muscle + chid + menopage + chol + cr + alt +
## hb + job_G + exer_G
## #Df LogLik Df Chisq Pr(>Chisq)
## 1 62 -20.5773
## 2 48 -1.5263 -14 38.102 0.0005013 ***
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
fit1_1선택
축소된 모형 하나 더 선택하여보자
deviance(fit1_3)-deviance(fit1_2)
## [1] 3.306539
lrtest(fit1_3,fit1_2)
## Likelihood ratio test
##
## Model 1: lscore_G ~ bmi + muscle + menopage + chol + cr + alt + hb + exer_G
## Model 2: lscore_G ~ bmi + muscle + menopage + chol + cr + alt + hb + job_G +
## exer_G
## #Df LogLik Df Chisq Pr(>Chisq)
## 1 52 -7.7814
## 2 50 -6.1281 -2 3.3065 0.1914
deviance(fit1_4)-deviance(fit1_3)
## [1] 0.4659935
lrtest(fit1_4,fit1_3)
## Likelihood ratio test
##
## Model 1: lscore_G ~ bmi + muscle + menopage + cr + alt + hb + exer_G
## Model 2: lscore_G ~ bmi + muscle + menopage + chol + cr + alt + hb + exer_G
## #Df LogLik Df Chisq Pr(>Chisq)
## 1 54 -8.0144
## 2 52 -7.7814 -2 0.466 0.7922
deviance(fit1_5)-deviance(fit1_4)
## [1] 4.786324
lrtest(fit1_5,fit1_4)
## Likelihood ratio test
##
## Model 1: lscore_G ~ muscle + menopage + cr + alt + hb + exer_G
## Model 2: lscore_G ~ bmi + muscle + menopage + cr + alt + hb + exer_G
## #Df LogLik Df Chisq Pr(>Chisq)
## 1 56 -10.4075
## 2 54 -8.0144 -2 4.7863 0.09134 .
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
deviance(fit1_6)-deviance(fit1_5)
## [1] 6.980622
lrtest(fit1_6,fit1_5)
## Likelihood ratio test
##
## Model 1: lscore_G ~ menopage + cr + alt + hb + exer_G
## Model 2: lscore_G ~ muscle + menopage + cr + alt + hb + exer_G
## #Df LogLik Df Chisq Pr(>Chisq)
## 1 58 -13.898
## 2 56 -10.408 -2 6.9806 0.03049 *
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
deviance(fit1_7)-deviance(fit1_5)
## [1] 12.01423
lrtest(fit1_7,fit1_5)
## Likelihood ratio test
##
## Model 1: lscore_G ~ menopage + cr + alt + hb
## Model 2: lscore_G ~ muscle + menopage + cr + alt + hb + exer_G
## #Df LogLik Df Chisq Pr(>Chisq)
## 1 60 -16.415
## 2 56 -10.408 -4 12.014 0.01725 *
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
deviance(fit1_8)-deviance(fit1_5)
## [1] 20.33961
lrtest(fit1_8,fit1_5)
## Likelihood ratio test
##
## Model 1: lscore_G ~ menopage + cr + hb
## Model 2: lscore_G ~ muscle + menopage + cr + alt + hb + exer_G
## #Df LogLik Df Chisq Pr(>Chisq)
## 1 62 -20.577
## 2 56 -10.408 -6 20.34 0.002409 **
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
summary(fit1_5)@ coef3
## Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
## (Intercept):1 66.57088295 33.8331452 1.9676232 0.04911140
## (Intercept):2 -684.02673778 892.8090232 -0.7661512 0.44358632
## muscle:1 -0.01700698 0.1601329 -0.1062054 0.91541936
## muscle:2 -3.36703004 5.9487909 -0.5660024 0.57139213
## menopage:1 -0.53978967 0.3122776 -1.7285573 0.08388836
## menopage:2 3.14524666 4.8226431 0.6521832 0.51428302
## cr:1 -15.09632079 9.6263012 -1.5682369 0.11682585
## cr:2 71.54149022 150.0435966 0.4768047 0.63350121
## alt:1 -0.14758700 0.1012155 -1.4581460 0.14480031
## alt:2 -1.32953761 3.1300048 -0.4247718 0.67100307
## hb:1 -2.18175766 1.3858636 -1.5742946 0.11541935
## hb:2 41.78536471 58.6241568 0.7127670 0.47598995
## exer_G2:1 -0.39732438 1.4672186 -0.2708011 0.78654404
## exer_G2:2 16.55601220 36.7468936 0.4505418 0.65231981
fit1_5 유의수준0.05하에 유의한 변수가 없으므로
최종적으로 fit1_1 선택하겠다.
fit1_1 모형
summary(fit1_1)@ coef3
## Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
## (Intercept):1 733.90553807 343.87118753 2.13424551 0.03282269
## (Intercept):2 -331.36213075 211.18733223 -1.56904359 0.11663778
## bmi:1 -3.12537399 1.57433781 -1.98519908 0.04712233
## bmi:2 -1.06286291 2.48820462 -0.42716057 0.66926238
## muscle:1 1.19855510 0.64340913 1.86281955 0.06248766
## muscle:2 -1.29775193 2.31560159 -0.56043835 0.57518048
## chid:1 -3.41221181 1.97314828 -1.72932357 0.08375120
## chid:2 0.15449595 5.04109951 0.03064727 0.97555084
## menopage:1 -5.35797722 2.62006253 -2.04498067 0.04085676
## menopage:2 1.37579641 1.58608041 0.86741908 0.38571243
## chol:1 0.09813986 0.06800762 1.44307167 0.14900028
## chol:2 -0.02653841 0.18603262 -0.14265463 0.88656295
## cr:1 -153.25240963 72.56825594 -2.11183813 0.03470034
## cr:2 45.00048055 75.52090512 0.59586787 0.55126350
## alt:1 -0.70636019 0.52563913 -1.34381204 0.17900917
## alt:2 -0.81237074 1.02412901 -0.79323086 0.42764333
## hb:1 -24.87063674 12.02995548 -2.06739225 0.03869721
## hb:2 22.29384591 15.16561737 1.47002561 0.14155482
## job_G2:1 -9.98673062 5.75716042 -1.73466256 0.08280059
## job_G2:2 -0.51407912 13.23942626 -0.03882941 0.96902640
## exer_G2:1 5.55481080 3.72195424 1.49244468 0.13558261
## exer_G2:2 7.79219881 9.83539911 0.79226056 0.42820876
fit1_1에서 유의한 변수
bmi “Body Mass Index”
menopage “폐경나이”
cr “크레아틴닌 수치”
hb “헤모글로빈 수치”
fit1_1에서 bmi 그래프
summary(esteo2$bmi)
## Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
## 13.32 20.60 22.61 22.03 24.13 27.92
par(mfrow = c(2, 2))
### fit1_1 job:1 (직업유),exer:1 (운동무) 에서 bmi 그래프
pi_1 <- exp(733.90554-3.12537*(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*mean(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*mean(esteo2$hb))/(1+exp(733.90554-3.12537*(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*mean(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*mean(esteo2$hb))+exp(-331.36213-1.06286*(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*mean(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*mean(esteo2$hb)))
y <- data.frame(esteo2$bmi,pi_1)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo2$bmi,pi_1)$esteo2.bmi, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo2.bmi,y$pi_1,type='l',xlab="bmi 수치", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(13.31,27.92),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=1,lwd=2, col=4)
par(new = T)
pi_2 <- exp(-331.36213-1.06286*(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*mean(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*mean(esteo2$hb))/(1+exp(733.90554-3.12537*(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*mean(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*mean(esteo2$hb))+exp(-331.36213-1.06286*(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*mean(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*mean(esteo2$hb)))
y <- data.frame(esteo2$bmi,pi_2)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo2$bmi,pi_2)$esteo2.bmi, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo2.bmi,y$pi_2,type='l',xlab="bmi 수치", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(13.31,27.92),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=3,lwd=2, col=3)
par(new = T)
pi_3 <- 1/(1+exp(733.90554-3.12537*(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*mean(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*mean(esteo2$hb))+exp(-331.36213-1.06286*(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*mean(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*mean(esteo2$hb)))
y <- data.frame(esteo2$bmi,pi_3)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo2$bmi,pi_3)$esteo2.bmi, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo2.bmi,y$pi_3,type='l',xlab="bmi 수치", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(13.31,27.92),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=5,lwd=2, col=6)
par(new = T)
legend("topright",bty='n', lty=c(1,3,5), c('lscore<q(0.3)','q(0.3)<lscore<q(0.7)','q(0.7)<lscore'), col=c(4,3,6), cex=0.8)
axis(side=1,at=seq(13,28,by=5))
axis(side=2,at=seq(0,1,by=0.2))
title(main= list("fit1_1 / 직업 유 / 운동 무에서 bmi", cex= 1, col = "coral",font = 3))
#fit1_1 job:2 (직업무),exer:2 (운동유) 에서 bmi 그래프
pi_1 <- exp(733.90554-3.12537*(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*mean(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*mean(esteo2$hb)-9.98673+5.55481)/(1+exp(733.90554-3.12537*(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*mean(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*mean(esteo2$hb)-9.98673+5.55481)+exp(-331.36213-1.06286*(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*mean(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*mean(esteo2$hb)-0.51408+7.79220))
y <- data.frame(esteo2$bmi,pi_1)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo2$bmi,pi_1)$esteo2.bmi, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo2.bmi,y$pi_1,type='l',xlab="bmi 수치", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(13.31,27.92),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=1,lwd=2, col=4)
par(new = T)
pi_2 <- exp(-331.36213-1.06286*(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*mean(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*mean(esteo2$hb)-0.51408+7.79220)/(1+exp(733.90554-3.12537*(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*mean(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*mean(esteo2$hb)-9.98673+5.55481)+exp(-331.36213-1.06286*(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*mean(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*mean(esteo2$hb)-0.51408+7.79220))
y <- data.frame(esteo2$bmi,pi_2)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo2$bmi,pi_2)$esteo2.bmi, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo2.bmi,y$pi_2,type='l',xlab="bmi 수치", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(13.31,27.92),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=3,lwd=2, col=3)
par(new = T)
pi_3 <- 1/((1+exp(733.90554-3.12537*(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*mean(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*mean(esteo2$hb)-9.98673+5.55481)+exp(-331.36213-1.06286*(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*mean(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*mean(esteo2$hb)-0.51408+7.79220)))
y <- data.frame(esteo2$bmi,pi_3)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo2$bmi,pi_3)$esteo2.bmi, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo2.bmi,y$pi_3,type='l',xlab="bmi 수치", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(13.31,27.92),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=5,lwd=2, col=6)
par(new = T)
legend("topright",bty='n', lty=c(1,3,5), c('lscore<q(0.3)','q(0.3)<lscore<q(0.7)','q(0.7)<lscore'), col=c(4,3,6), cex=0.8)
axis(side=1,at=seq(13,28,by=5))
axis(side=2,at=seq(0,1,by=0.2))
title(main= list("fit1_1 / 직업 무 / 운동 유에서 bmi", cex= 1, col = "coral",font = 3))
#fit1_1 job:1 (직업유),exer:2 (운동유) 에서 bmi 그래프
pi_1 <- exp(733.90554-3.12537*(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*mean(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*mean(esteo2$hb)+5.55481)/(1+exp(733.90554-3.12537*(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*mean(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*mean(esteo2$hb)+5.55481)+exp(-331.36213-1.06286*(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*mean(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*mean(esteo2$hb)+7.79220))
y <- data.frame(esteo2$bmi,pi_1)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo2$bmi,pi_1)$esteo2.bmi, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo2.bmi,y$pi_1,type='l',xlab="bmi 수치", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(13.31,27.92),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=1,lwd=2, col=4)
par(new = T)
pi_2 <- exp(-331.36213-1.06286*(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*mean(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*mean(esteo2$hb)+7.79220)/(1+exp(733.90554-3.12537*(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*mean(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*mean(esteo2$hb)+5.55481)+exp(-331.36213-1.06286*(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*mean(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*mean(esteo2$hb)+7.79220))
y <- data.frame(esteo2$bmi,pi_2)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo2$bmi,pi_2)$esteo2.bmi, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo2.bmi,y$pi_2,type='l',xlab="bmi 수치", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(13.31,27.92),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=3,lwd=2, col=3)
par(new = T)
pi_3 <- 1/((1+exp(733.90554-3.12537*(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*mean(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*mean(esteo2$hb)+5.55481)+exp(-331.36213-1.06286*(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*mean(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*mean(esteo2$hb)+7.79220)))
y <- data.frame(esteo2$bmi,pi_3)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo2$bmi,pi_3)$esteo2.bmi, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo2.bmi,y$pi_3,type='l',xlab="bmi 수치", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(13.31,27.92),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=5,lwd=2, col=6)
par(new = T)
legend("topright",bty='n', lty=c(1,3,5), c('lscore<q(0.3)','q(0.3)<lscore<q(0.7)','q(0.7)<lscore'), col=c(4,3,6), cex=0.8)
axis(side=1,at=seq(13,28,by=5))
axis(side=2,at=seq(0,1,by=0.2))
title(main= list("fit1_1 / 직업 유 / 운동 유에서 bmi", cex= 1, col = "coral",font = 3))
#fit1_1 job:2 (직업무),exer:1 (운동무) 에서 bmi 그래프
pi_1 <- exp(733.90554-3.12537*(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*mean(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*mean(esteo2$hb)-9.98673)/(1+exp(733.90554-3.12537*(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*mean(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*mean(esteo2$hb)-9.98673)+exp(-331.36213-1.06286*(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*mean(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*mean(esteo2$hb)-0.51408))
y <- data.frame(esteo2$bmi,pi_1)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo2$bmi,pi_1)$esteo2.bmi, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo2.bmi,y$pi_1,type='l',xlab="bmi 수치", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(13.31,27.92),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=1,lwd=2, col=4)
par(new = T)
pi_2 <- exp(-331.36213-1.06286*(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*mean(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*mean(esteo2$hb)-0.51408)/(1+exp(733.90554-3.12537*(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*mean(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*mean(esteo2$hb)-9.98673)+exp(-331.36213-1.06286*(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*mean(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*mean(esteo2$hb)-0.51408))
y <- data.frame(esteo2$bmi,pi_2)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo2$bmi,pi_2)$esteo2.bmi, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo2.bmi,y$pi_2,type='l',xlab="bmi 수치", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(13.31,27.92),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=3,lwd=2, col=3)
par(new = T)
pi_3 <- 1/((1+exp(733.90554-3.12537*(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*mean(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*mean(esteo2$hb)-9.98673)+exp(-331.36213-1.06286*(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*mean(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*mean(esteo2$hb)-0.51408)))
y <- data.frame(esteo2$bmi,pi_3)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo2$bmi,pi_3)$esteo2.bmi, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo2.bmi,y$pi_3,type='l',xlab="bmi 수치", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(13.31,27.92),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=5,lwd=2, col=6)
par(new = T)
legend("topright",bty='n', lty=c(1,3,5), c('lscore<q(0.3)','q(0.3)<lscore<q(0.7)','q(0.7)<lscore'), col=c(4,3,6), cex=0.8)
axis(side=1,at=seq(13,28,by=5))
axis(side=2,at=seq(0,1,by=0.2))
title(main= list("fit1_1 / 직업 무 / 운동 무에서 bmi", cex= 1, col = "coral",font = 3))
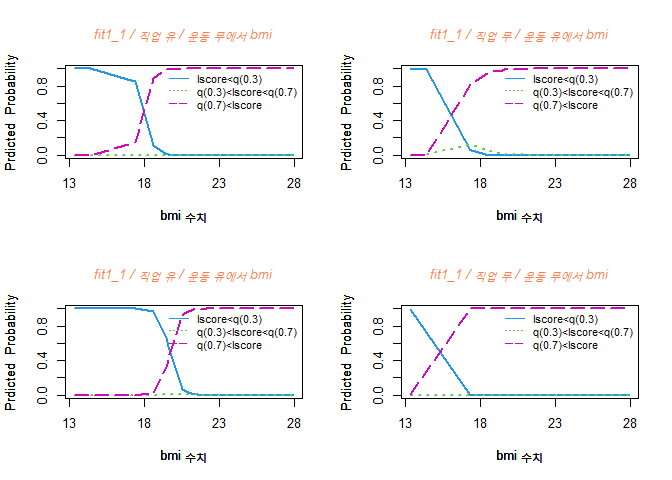
전반적으로 bmi 수치가 높을 수록 Y=3 그룹일 확률이 높으며, bmi 수치가 낮을수록 Y=1 그룹일 확률이 높다.
bmi가 높을수록 왜 골밀도가 높은지 이해가 안간다.
bmi 기준을 확인하여 보자 bmi 수치가 18.5이하는 저체중이며 25이상이 비만이라고 한다.
bmi 수치가 18 이전에는 Y=1 그룹일 확률이 높은 것으로 보아 저체중이 비만보다 골밀도에 큰 영향을 준다고 볼 수 있다.
직업있고 운동하는 그룹이 Y=1과 Y=3간에 교차가 제일 늦게 일어나는 것을 확인할 수 있으며 정상범위인 18에서 23 사이에 교차가 일어난다, 직업없고 운동 안하는 집단이 가장 빠르고 급격하게 교차가 일어나는 것을 볼 수 있다.
fit1_1에서 menopage 그래프
par(mfrow = c(2, 2))
summary(esteo2$menopage)
## Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
## 37.00 46.00 50.00 48.26 50.50 57.00
summary(fit1_1)
##
## Call:
## vglm(formula = lscore_G ~ bmi + muscle + chid + menopage + chol +
## cr + alt + hb + job_G + exer_G, family = multinomial(refLevel = "3"),
## data = esteo2)
##
## Coefficients:
## Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
## (Intercept):1 733.90554 343.87119 2.134 0.0328 *
## (Intercept):2 -331.36213 211.18733 NA NA
## bmi:1 -3.12537 1.57434 NA NA
## bmi:2 -1.06286 2.48820 NA NA
## muscle:1 1.19856 0.64341 1.863 0.0625 .
## muscle:2 -1.29775 2.31560 NA NA
## chid:1 -3.41221 1.97315 NA NA
## chid:2 0.15450 5.04110 0.031 0.9756
## menopage:1 -5.35798 2.62006 NA NA
## menopage:2 1.37580 1.58608 0.867 0.3857
## chol:1 0.09814 0.06801 NA NA
## chol:2 -0.02654 0.18603 NA NA
## cr:1 -153.25241 72.56826 NA NA
## cr:2 45.00048 75.52091 0.596 0.5513
## alt:1 -0.70636 0.52564 NA NA
## alt:2 -0.81237 1.02413 NA NA
## hb:1 -24.87064 12.02996 NA NA
## hb:2 22.29385 15.16562 1.470 0.1416
## job_G2:1 -9.98673 5.75716 NA NA
## job_G2:2 -0.51408 13.23943 -0.039 0.9690
## exer_G2:1 5.55481 3.72195 1.492 0.1356
## exer_G2:2 7.79220 9.83540 0.792 0.4282
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## Names of linear predictors: log(mu[,1]/mu[,3]), log(mu[,2]/mu[,3])
##
## Residual deviance: 3.0527 on 48 degrees of freedom
##
## Log-likelihood: -1.5263 on 48 degrees of freedom
##
## Number of Fisher scoring iterations: 16
##
## Warning: Hauck-Donner effect detected in the following estimate(s):
## '(Intercept):2', 'bmi:1', 'bmi:2', 'muscle:2', 'chid:1', 'menopage:1', 'chol:1', 'chol:2', 'cr:1', 'alt:1', 'alt:2', 'hb:1', 'job_G2:1'
##
##
## Reference group is level 3 of the response
#fit1_1 job:1 (직업유),exer:1 (운동무) 에서 menopage 그래프
pi_1 <- exp(733.90554-3.12537*mean(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*mean(esteo2$hb))/(1+exp(733.90554-3.12537*mean(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*mean(esteo2$hb))+exp(-331.36213-1.06286*mean(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*mean(esteo2$hb)))
y <- data.frame(esteo2$menopage,pi_1)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo2$menopage,pi_1)$esteo2.menopage, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo2.menopage,y$pi_1,type='l',xlab="menopage", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(37,57),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=1,lwd=2, col=4)
par(new = T)
pi_2 <- exp(-331.36213-1.06286*mean(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*mean(esteo2$hb))/(1+exp(733.90554-3.12537*mean(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*mean(esteo2$hb))+exp(-331.36213-1.06286*mean(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*mean(esteo2$hb)))
y <- data.frame(esteo2$menopage,pi_2)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo2$menopage,pi_2)$esteo2.menopage, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo2.menopage,y$pi_2,type='l',xlab="menopage", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(37,57),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=3,lwd=2, col=3)
par(new = T)
pi_3 <- 1/(1+exp(733.90554-3.12537*mean(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*mean(esteo2$hb))+exp(-331.36213-1.06286*mean(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*mean(esteo2$hb)))
y <- data.frame(esteo2$menopage,pi_3)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo2$menopage,pi_3)$esteo2.menopage, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo2.menopage,y$pi_3,type='l',xlab="menopage", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(37,57),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=5,lwd=2, col=6)
par(new = T)
legend("topright",bty='n', lty=c(1,3,5), c('lscore<q(0.3)','q(0.3)<lscore<q(0.7)','q(0.7)<lscore'), col=c(4,3,6), cex=0.8)
axis(side=1,at=seq(35,60,by=5))
axis(side=2,at=seq(0,1,by=0.2))
title(main= list("fit1_1 / 직업 유 / 운동 무에서 menopage", cex= 1, col = "coral",font = 3))
#fit1_1 job:2 (직업무), exer:2 (운동유) 에서 menopage 그래프
pi_1 <- exp(733.90554-3.12537*mean(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*mean(esteo2$hb)-9.98673+5.55481)/(1+exp(733.90554-3.12537*mean(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*mean(esteo2$hb)-9.98673+5.55481)+exp(-331.36213-1.06286*mean(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*mean(esteo2$hb)-0.51408+7.79220))
y <- data.frame(esteo2$menopage,pi_1)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo2$menopage,pi_1)$esteo2.menopage, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo2.menopage,y$pi_1,type='l',xlab="menopage", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(37,57),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=1,lwd=2, col=4)
par(new = T)
pi_2 <- exp(-331.36213-1.06286*mean(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*mean(esteo2$hb)-0.51408+7.79220)/(1+exp(733.90554-3.12537*mean(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*mean(esteo2$hb)-9.98673+5.55481)+exp(-331.36213-1.06286*mean(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*mean(esteo2$hb)-0.51408+7.79220))
y <- data.frame(esteo2$menopage,pi_2)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo2$menopage,pi_2)$esteo2.menopage, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo2.menopage,y$pi_2,type='l',xlab="menopage", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(37,57),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=3,lwd=2, col=3)
par(new = T)
pi_3 <- 1/(1+exp(733.90554-3.12537*mean(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*mean(esteo2$hb)-9.98673+5.55481)+exp(-331.36213-1.06286*mean(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*mean(esteo2$hb)-0.51408+7.79220))
y <- data.frame(esteo2$menopage,pi_3)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo2$menopage,pi_3)$esteo2.menopage, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo2.menopage,y$pi_3,type='l',xlab="menopage", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(37,57),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=5,lwd=2, col=6)
par(new = T)
legend("topright",bty='n', lty=c(1,3,5), c('lscore<q(0.3)','q(0.3)<lscore<q(0.7)','q(0.7)<lscore'), col=c(4,3,6), cex=0.8)
axis(side=1,at=seq(35,60,by=5))
axis(side=2,at=seq(0,1,by=0.2))
title(main= list("fit1_1 / 직업 무 / 운동 유에서 menopage", cex= 1, col = "coral",font = 3))
#fit1_1job:1 (직업유),exer:2 (운동유) 에서 menopage 그래프
pi_1 <- exp(733.90554-3.12537*mean(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*mean(esteo2$hb)+5.55481)/(1+exp(733.90554-3.12537*mean(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*mean(esteo2$hb)+5.55481)+exp(-331.36213-1.06286*mean(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*mean(esteo2$hb)+7.79220))
y <- data.frame(esteo2$menopage,pi_1)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo2$menopage,pi_1)$esteo2.menopage, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo2.menopage,y$pi_1,type='l',xlab="menopage", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(37,57),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=1,lwd=2, col=4)
par(new = T)
pi_2 <- exp(-331.36213-1.06286*mean(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*mean(esteo2$hb)+7.79220)/(1+exp(733.90554-3.12537*mean(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*mean(esteo2$hb)+5.55481)+exp(-331.36213-1.06286*mean(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*mean(esteo2$hb)+7.79220))
y <- data.frame(esteo2$menopage,pi_2)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo2$menopage,pi_2)$esteo2.menopage, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo2.menopage,y$pi_2,type='l',xlab="menopage", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(37,57),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=3,lwd=2, col=3)
par(new = T)
pi_3 <- 1/(1+exp(733.90554-3.12537*mean(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*mean(esteo2$hb)+5.55481)+exp(-331.36213-1.06286*mean(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*mean(esteo2$hb)+7.79220))
y <- data.frame(esteo2$menopage,pi_3)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo2$menopage,pi_3)$esteo2.menopage, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo2.menopage,y$pi_3,type='l',xlab="menopage", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(37,57),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=5,lwd=2, col=6)
par(new = T)
legend("topright",bty='n', lty=c(1,3,5), c('lscore<q(0.3)','q(0.3)<lscore<q(0.7)','q(0.7)<lscore'), col=c(4,3,6), cex=0.8)
axis(side=1,at=seq(35,60,by=5))
axis(side=2,at=seq(0,1,by=0.2))
title(main= list("fit1_1 / 직업 유 / 운동 유에서 menopage", cex= 1, col = "coral",font = 3))
#fit1_1 job:2 (직업무), exer:1 (운동무) 에서 menopage 그래프
pi_1 <- exp(733.90554-3.12537*mean(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*mean(esteo2$hb)-9.98673)/(1+exp(733.90554-3.12537*mean(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*mean(esteo2$hb)-9.98673)+exp(-331.36213-1.06286*mean(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*mean(esteo2$hb)-0.51408))
y <- data.frame(esteo2$menopage,pi_1)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo2$menopage,pi_1)$esteo2.menopage, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo2.menopage,y$pi_1,type='l',xlab="menopage", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(37,57),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=1,lwd=2, col=4)
par(new = T)
pi_2 <- exp(-331.36213-1.06286*mean(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*mean(esteo2$hb)-0.51408)/(1+exp(733.90554-3.12537*mean(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*mean(esteo2$hb)-9.98673)+exp(-331.36213-1.06286*mean(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*mean(esteo2$hb)-0.51408))
y <- data.frame(esteo2$menopage,pi_2)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo2$menopage,pi_2)$esteo2.menopage, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo2.menopage,y$pi_2,type='l',xlab="menopage", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(37,57),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=3,lwd=2, col=3)
par(new = T)
pi_3 <- 1/(1+exp(733.90554-3.12537*mean(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*mean(esteo2$hb)-9.98673)+exp(-331.36213-1.06286*mean(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*mean(esteo2$hb)-0.51408))
y <- data.frame(esteo2$menopage,pi_3)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo2$menopage,pi_3)$esteo2.menopage, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo2.menopage,y$pi_3,type='l',xlab="menopage", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(37,57),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=5,lwd=2, col=6)
par(new = T)
legend("topright",bty='n', lty=c(1,3,5), c('lscore<q(0.3)','q(0.3)<lscore<q(0.7)','q(0.7)<lscore'), col=c(4,3,6), cex=0.8)
axis(side=1,at=seq(35,60,by=5))
axis(side=2,at=seq(0,1,by=0.2))
title(main= list("fit1_1/ 직업 무 / 운동 무에서 menopage", cex= 1, col = "coral",font = 3))
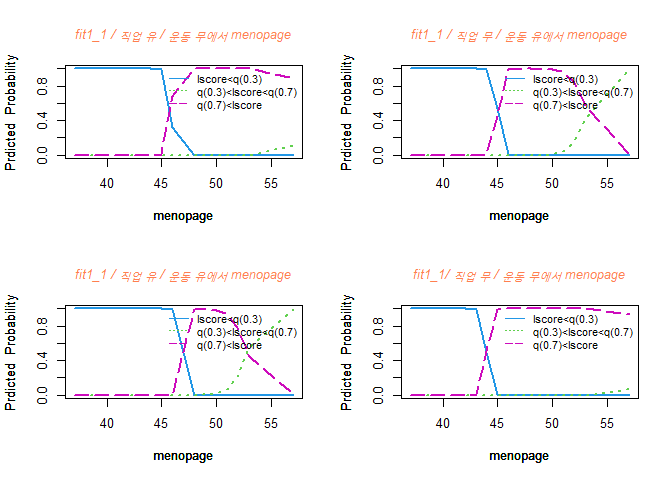
전반적으로 폐경 후 나이가 증가함에 따라서 Y=3 그룹일 확률이 높으며, 폐경 후 나이가 어릴 수록 Y=1 그룹일 확률이 높다.
이것도 bmi 수치와 마찬가지로 나이가 증가함에 따라서 왜 골밀도가 더 낮은 집단일 확률이 더 낮아지는지 의아아했다.
폐경 후 나이의 기준을 살펴 보았다. 정상 폐경 나이가 48~52세이며 평균 폐경 연령이 49.7세이다.
조기 폐경을 한 그룹일 경우에 골밀도가 낮은 그룹에 속할 확률이 높은 것으로 볼 수 있을 것 같다.
하지만, 운동을 하는 그룹에서 폐경 후 나이가 증가함에 따라 Y=3 그룹일 확률이 감소하는 경향을 보였다.
운동을 하는 그룹에서 직업까지 가진 그룹이면 Y=3 그룹일 확률이 더 빠르게 감소하는 것을 볼 수 있다.
fit1_1에서 cr 그래프
par(mfrow = c(2, 2))
summary(esteo2$cr)
## Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
## 0.6000 0.7000 0.7000 0.7657 0.8000 1.2000
summary(fit1_1)
##
## Call:
## vglm(formula = lscore_G ~ bmi + muscle + chid + menopage + chol +
## cr + alt + hb + job_G + exer_G, family = multinomial(refLevel = "3"),
## data = esteo2)
##
## Coefficients:
## Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
## (Intercept):1 733.90554 343.87119 2.134 0.0328 *
## (Intercept):2 -331.36213 211.18733 NA NA
## bmi:1 -3.12537 1.57434 NA NA
## bmi:2 -1.06286 2.48820 NA NA
## muscle:1 1.19856 0.64341 1.863 0.0625 .
## muscle:2 -1.29775 2.31560 NA NA
## chid:1 -3.41221 1.97315 NA NA
## chid:2 0.15450 5.04110 0.031 0.9756
## menopage:1 -5.35798 2.62006 NA NA
## menopage:2 1.37580 1.58608 0.867 0.3857
## chol:1 0.09814 0.06801 NA NA
## chol:2 -0.02654 0.18603 NA NA
## cr:1 -153.25241 72.56826 NA NA
## cr:2 45.00048 75.52091 0.596 0.5513
## alt:1 -0.70636 0.52564 NA NA
## alt:2 -0.81237 1.02413 NA NA
## hb:1 -24.87064 12.02996 NA NA
## hb:2 22.29385 15.16562 1.470 0.1416
## job_G2:1 -9.98673 5.75716 NA NA
## job_G2:2 -0.51408 13.23943 -0.039 0.9690
## exer_G2:1 5.55481 3.72195 1.492 0.1356
## exer_G2:2 7.79220 9.83540 0.792 0.4282
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## Names of linear predictors: log(mu[,1]/mu[,3]), log(mu[,2]/mu[,3])
##
## Residual deviance: 3.0527 on 48 degrees of freedom
##
## Log-likelihood: -1.5263 on 48 degrees of freedom
##
## Number of Fisher scoring iterations: 16
##
## Warning: Hauck-Donner effect detected in the following estimate(s):
## '(Intercept):2', 'bmi:1', 'bmi:2', 'muscle:2', 'chid:1', 'menopage:1', 'chol:1', 'chol:2', 'cr:1', 'alt:1', 'alt:2', 'hb:1', 'job_G2:1'
##
##
## Reference group is level 3 of the response
#fit1_1 job:1 (직업유),exer:1 (운동무) 에서 cr 그래프
pi_1 <- exp(733.90554-3.12537*mean(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*mean(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*mean(esteo2$hb))/(1+exp(733.90554-3.12537*mean(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*mean(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*mean(esteo2$hb))+exp(-331.36213-1.06286*mean(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*mean(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*mean(esteo2$hb)))
y <- data.frame(esteo2$cr,pi_1)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo2$cr,pi_1)$esteo2.cr, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo2.cr,y$pi_1,type='l',xlab="cr 수치", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(0.6,1.2),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=1,lwd=2, col=4)
par(new = T)
pi_2 <- exp(-331.36213-1.06286*mean(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*mean(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*mean(esteo2$hb))/(1+exp(733.90554-3.12537*mean(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*mean(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*mean(esteo2$hb))+exp(-331.36213-1.06286*mean(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*mean(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*mean(esteo2$hb)))
y <- data.frame(esteo2$cr,pi_2)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo2$cr,pi_2)$esteo2.cr, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo2.cr,y$pi_2,type='l',xlab="cr 수치", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(0.6,1.2),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=3,lwd=2, col=3)
par(new = T)
pi_3 <- 1/(1+exp(733.90554-3.12537*mean(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*mean(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*mean(esteo2$hb))+exp(-331.36213-1.06286*mean(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*mean(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*mean(esteo2$hb)))
y <- data.frame(esteo2$cr,pi_3)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo2$cr,pi_3)$esteo2.cr, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo2.cr,y$pi_3,type='l',xlab="cr 수치", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(0.6,1.2),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=5,lwd=2, col=6)
par(new = T)
legend("topright",bty='n', lty=c(1,3,5), c('lscore<q(0.3)','q(0.3)<lscore<q(0.7)','q(0.7)<lscore'), col=c(4,3,6), cex=0.8)
axis(side=1,at=seq(0.5,1.5,by=0.1))
axis(side=2,at=seq(0,1,by=0.2))
title(main= list("fit1_1/ 직업 유 / 운동 무에서 cr", cex= 1, col = "coral",font = 3))
#fit1_1 job:2 (직업무),exer:2 (운동유) 에서 cr 그래프
pi_1 <- exp(733.90554-3.12537*mean(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*mean(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*mean(esteo2$hb)-9.98673+5.55481)/(1+exp(733.90554-3.12537*mean(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*mean(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*mean(esteo2$hb)-9.98673+5.55481)+exp(-331.36213-1.06286*mean(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*mean(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*mean(esteo2$hb)-0.51408+7.79220))
y <- data.frame(esteo2$cr,pi_1)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo2$cr,pi_1)$esteo2.cr, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo2.cr,y$pi_1,type='l',xlab="cr 수치", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(0.6,1.2),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=1,lwd=2, col=4)
par(new = T)
pi_2 <- exp(-331.36213-1.06286*mean(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*mean(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*mean(esteo2$hb)-0.51408+7.79220)/(1+exp(733.90554-3.12537*mean(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*mean(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*mean(esteo2$hb)-9.98673+5.55481)+exp(-331.36213-1.06286*mean(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*mean(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*mean(esteo2$hb)-0.51408+7.79220))
y <- data.frame(esteo2$cr,pi_2)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo2$cr,pi_2)$esteo2.cr, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo2.cr,y$pi_2,type='l',xlab="cr 수치", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(0.6,1.2),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=3,lwd=2, col=3)
par(new = T)
pi_3 <- 1/(1+exp(733.90554-3.12537*mean(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*mean(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*mean(esteo2$hb)-9.98673+5.55481)+exp(-331.36213-1.06286*mean(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*mean(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*mean(esteo2$hb)-0.51408+7.79220))
y <- data.frame(esteo2$cr,pi_3)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo2$cr,pi_3)$esteo2.cr, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo2.cr,y$pi_3,type='l',xlab="cr 수치", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(0.6,1.2),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=5,lwd=2, col=6)
par(new = T)
legend("topright",bty='n', lty=c(1,3,5), c('lscore<q(0.3)','q(0.3)<lscore<q(0.7)','q(0.7)<lscore'), col=c(4,3,6), cex=0.8)
axis(side=1,at=seq(0.5,1.5,by=0.1))
axis(side=2,at=seq(0,1,by=0.2))
title(main= list("fit1_1 / 직업 무 / 운동 유에서 cr", cex= 1, col = "coral",font = 3))
#fit1_1 job:1 (직업유),exer:2 (운동유) 에서 cr 그래프
pi_1 <- exp(733.90554-3.12537*mean(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*mean(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*mean(esteo2$hb)+5.55481)/(1+exp(733.90554-3.12537*mean(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*mean(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*mean(esteo2$hb)+5.55481)+exp(-331.36213-1.06286*mean(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*mean(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*mean(esteo2$hb)+7.79220))
y <- data.frame(esteo2$cr,pi_1)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo2$cr,pi_1)$esteo2.cr, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo2.cr,y$pi_1,type='l',xlab="cr 수치", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(0.6,1.2),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=1,lwd=2, col=4)
par(new = T)
pi_2 <- exp(-331.36213-1.06286*mean(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*mean(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*mean(esteo2$hb)+7.79220)/(1+exp(733.90554-3.12537*mean(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*mean(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*mean(esteo2$hb)+5.55481)+exp(-331.36213-1.06286*mean(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*mean(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*mean(esteo2$hb)+7.79220))
y <- data.frame(esteo2$cr,pi_2)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo2$cr,pi_2)$esteo2.cr, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo2.cr,y$pi_2,type='l',xlab="cr 수치", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(0.6,1.2),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=3,lwd=2, col=3)
par(new = T)
pi_3 <- 1/(1+exp(733.90554-3.12537*mean(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*mean(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*mean(esteo2$hb)+5.55481)+exp(-331.36213-1.06286*mean(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*mean(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*mean(esteo2$hb)+7.79220))
y <- data.frame(esteo2$cr,pi_3)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo2$cr,pi_3)$esteo2.cr, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo2.cr,y$pi_3,type='l',xlab="cr 수치", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(0.6,1.2),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=5,lwd=2, col=6)
par(new = T)
legend("topright",bty='n', lty=c(1,3,5), c('lscore<q(0.3)','q(0.3)<lscore<q(0.7)','q(0.7)<lscore'), col=c(4,3,6), cex=0.8)
axis(side=1,at=seq(0.5,1.5,by=0.1))
axis(side=2,at=seq(0,1,by=0.2))
title(main= list("fit1_1 / 직업 유 / 운동 유에서 cr", cex= 1, col = "coral",font = 3))
#fit1_1 job:2 (직업무),exer:1 (운동무) 에서 cr 그래프
pi_1 <- exp(733.90554-3.12537*mean(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*mean(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*mean(esteo2$hb)-9.98673)/(1+exp(733.90554-3.12537*mean(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*mean(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*mean(esteo2$hb)-9.98673)+exp(-331.36213-1.06286*mean(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*mean(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*mean(esteo2$hb)-0.51408))
y <- data.frame(esteo2$cr,pi_1)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo2$cr,pi_1)$esteo2.cr, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo2.cr,y$pi_1,type='l',xlab="cr 수치", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(0.6,1.2),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=1,lwd=2, col=4)
par(new = T)
pi_2 <- exp(-331.36213-1.06286*mean(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*mean(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*mean(esteo2$hb)-0.51408)/(1+exp(733.90554-3.12537*mean(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*mean(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*mean(esteo2$hb)-9.98673)+exp(-331.36213-1.06286*mean(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*mean(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*mean(esteo2$hb)-0.51408))
y <- data.frame(esteo2$cr,pi_2)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo2$cr,pi_2)$esteo2.cr, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo2.cr,y$pi_2,type='l',xlab="cr 수치", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(0.6,1.2),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=3,lwd=2, col=3)
par(new = T)
pi_3 <- 1/(1+exp(733.90554-3.12537*mean(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*mean(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*mean(esteo2$hb)-9.98673)+exp(-331.36213-1.06286*mean(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*mean(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*mean(esteo2$hb)-0.51408))
y <- data.frame(esteo2$cr,pi_3)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo2$cr,pi_3)$esteo2.cr, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo2.cr,y$pi_3,type='l',xlab="cr 수치", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(0.6,1.2),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=5,lwd=2, col=6)
par(new = T)
legend("topright",bty='n', lty=c(1,3,5), c('lscore<q(0.3)','q(0.3)<lscore<q(0.7)','q(0.7)<lscore'), col=c(4,3,6), cex=0.8)
axis(side=1,at=seq(0.5,1.5,by=0.1))
axis(side=2,at=seq(0,1,by=0.2))
title(main= list("fit1_1 / 직업 무 / 운동 무에서 cr", cex= 1, col = "coral",font = 3))
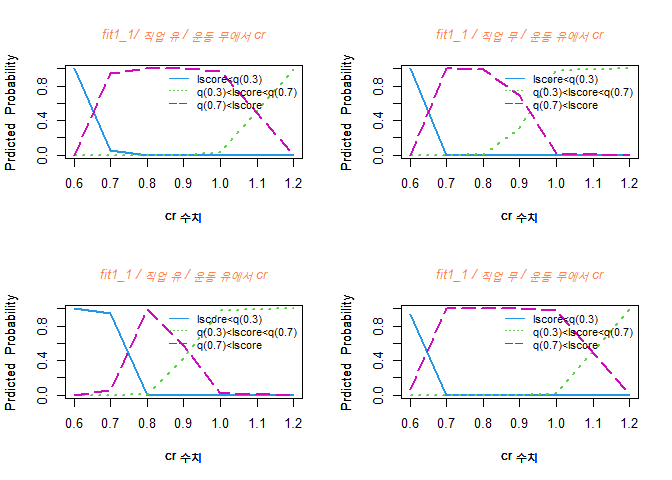
cr 수치가 높을수록 대체적으로 Y=3 그룹에 속할 확률이 높으며, 어느 순간 Y=2 그룹에 속할 확률이 더 높아진다.
아무래도 cr 정상범위에 있는 사람일 수록 골밀도가 높은 것을 알 수 있다.
cr 수치가 정상범위에서 벗어나면 골밀도 수치가 낮은 그룹에 속하게 되는데 cr 수치가 낮은 것이 골밀도 수치가 더 낮은 그룹에 속하게 되는 것을 볼 수 있다.
fit1_1에서 hb 그래프
par(mfrow = c(2, 2))
summary(esteo2$hb)
## Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
## 10.20 12.10 12.60 12.61 13.35 14.20
summary(fit1_1)
##
## Call:
## vglm(formula = lscore_G ~ bmi + muscle + chid + menopage + chol +
## cr + alt + hb + job_G + exer_G, family = multinomial(refLevel = "3"),
## data = esteo2)
##
## Coefficients:
## Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
## (Intercept):1 733.90554 343.87119 2.134 0.0328 *
## (Intercept):2 -331.36213 211.18733 NA NA
## bmi:1 -3.12537 1.57434 NA NA
## bmi:2 -1.06286 2.48820 NA NA
## muscle:1 1.19856 0.64341 1.863 0.0625 .
## muscle:2 -1.29775 2.31560 NA NA
## chid:1 -3.41221 1.97315 NA NA
## chid:2 0.15450 5.04110 0.031 0.9756
## menopage:1 -5.35798 2.62006 NA NA
## menopage:2 1.37580 1.58608 0.867 0.3857
## chol:1 0.09814 0.06801 NA NA
## chol:2 -0.02654 0.18603 NA NA
## cr:1 -153.25241 72.56826 NA NA
## cr:2 45.00048 75.52091 0.596 0.5513
## alt:1 -0.70636 0.52564 NA NA
## alt:2 -0.81237 1.02413 NA NA
## hb:1 -24.87064 12.02996 NA NA
## hb:2 22.29385 15.16562 1.470 0.1416
## job_G2:1 -9.98673 5.75716 NA NA
## job_G2:2 -0.51408 13.23943 -0.039 0.9690
## exer_G2:1 5.55481 3.72195 1.492 0.1356
## exer_G2:2 7.79220 9.83540 0.792 0.4282
## ---
## Signif. codes: 0 '***' 0.001 '**' 0.01 '*' 0.05 '.' 0.1 ' ' 1
##
## Names of linear predictors: log(mu[,1]/mu[,3]), log(mu[,2]/mu[,3])
##
## Residual deviance: 3.0527 on 48 degrees of freedom
##
## Log-likelihood: -1.5263 on 48 degrees of freedom
##
## Number of Fisher scoring iterations: 16
##
## Warning: Hauck-Donner effect detected in the following estimate(s):
## '(Intercept):2', 'bmi:1', 'bmi:2', 'muscle:2', 'chid:1', 'menopage:1', 'chol:1', 'chol:2', 'cr:1', 'alt:1', 'alt:2', 'hb:1', 'job_G2:1'
##
##
## Reference group is level 3 of the response
#fit1_1 job:1 (직업유),exer:1 (운동무) 에서 hb 그래프
pi_1 <- exp(733.90554-3.12537*mean(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*mean(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*(esteo2$hb))/(1+exp(733.90554-3.12537*mean(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*mean(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*(esteo2$hb))+exp(-331.36213-1.06286*mean(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*mean(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*(esteo2$hb)))
y <- data.frame(esteo2$hb,pi_1)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo2$hb,pi_1)$esteo2.hb, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo2.hb,y$pi_1,type='l',xlab="hb 수치", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(10.2,14.2),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=1,lwd=2, col=4)
par(new = T)
pi_2 <- exp(-331.36213-1.06286*mean(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*mean(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*(esteo2$hb))/(1+exp(733.90554-3.12537*mean(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*mean(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*(esteo2$hb))+exp(-331.36213-1.06286*mean(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*mean(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*(esteo2$hb)))
y <- data.frame(esteo2$hb,pi_2)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo2$hb,pi_2)$esteo2.hb, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo2.hb,y$pi_2,type='l',xlab="hb 수치", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(10.2,14.2),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=3,lwd=2, col=3)
par(new = T)
pi_3 <- 1/(1+exp(733.90554-3.12537*mean(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*mean(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*(esteo2$hb))+exp(-331.36213-1.06286*mean(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*mean(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*(esteo2$hb)))
y <- data.frame(esteo2$hb,pi_3)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo2$hb,pi_3)$esteo2.hb, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo2.hb,y$pi_3,type='l',xlab="hb 수치", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(10.2,14.2),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=5,lwd=2, col=6)
par(new = T)
legend("topright",bty='n', lty=c(1,3,5), c('lscore<q(0.3)','q(0.3)<lscore<q(0.7)','q(0.7)<lscore'), col=c(4,3,6), cex=0.8)
axis(side=1,at=seq(10,15,by=1))
axis(side=2,at=seq(0,1,by=0.2))
title(main= list("fit1_1 / 직업 유 / 운동 무에서 hb", cex= 1, col = "coral",font = 3))
#fit1_1 job:2 (직업무),exer:2 (운동유) 에서 hb 그래프
pi_1 <- exp(733.90554-3.12537*mean(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*mean(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*(esteo2$hb)-9.98673+5.55481)/(1+exp(733.90554-3.12537*mean(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*mean(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*(esteo2$hb)-9.98673+5.55481)+exp(-331.36213-1.06286*mean(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*mean(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*(esteo2$hb)-0.51408+7.79220))
y <- data.frame(esteo2$hb,pi_1)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo2$hb,pi_1)$esteo2.hb, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo2.hb,y$pi_1,type='l',xlab="hb 수치", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(10.2,14.2),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=1,lwd=2, col=4)
par(new = T)
pi_2 <- exp(-331.36213-1.06286*mean(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*mean(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*(esteo2$hb)-0.51408+7.79220)/(1+exp(733.90554-3.12537*mean(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*mean(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*(esteo2$hb)-9.98673+5.55481)+exp(-331.36213-1.06286*mean(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*mean(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*(esteo2$hb)-0.51408+7.79220))
y <- data.frame(esteo2$hb,pi_2)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo2$hb,pi_2)$esteo2.hb, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo2.hb,y$pi_2,type='l',xlab="hb 수치", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(10.2,14.2),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=3,lwd=2, col=3)
par(new = T)
pi_3 <- 1/(1+exp(733.90554-3.12537*mean(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*mean(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*(esteo2$hb)-9.98673+5.55481)+exp(-331.36213-1.06286*mean(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*mean(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*(esteo2$hb)-0.51408+7.79220))
y <- data.frame(esteo2$hb,pi_3)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo2$hb,pi_3)$esteo2.hb, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo2.hb,y$pi_3,type='l',xlab="hb 수치", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(10.2,14.2),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=5,lwd=2, col=6)
par(new = T)
legend("topright",bty='n', lty=c(1,3,5), c('lscore<q(0.3)','q(0.3)<lscore<q(0.7)','q(0.7)<lscore'), col=c(4,3,6), cex=0.8)
axis(side=1,at=seq(10,15,by=1))
axis(side=2,at=seq(0,1,by=0.2))
title(main= list("fit1_1 / 직업 무 / 운동 유에서 hb", cex= 1, col = "coral",font = 3))
#fit1_1 job:1 (직업유),exer:2 (운동유) 에서 hb 그래프
pi_1 <- exp(733.90554-3.12537*mean(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*mean(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*(esteo2$hb)+5.55481)/(1+exp(733.90554-3.12537*mean(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*mean(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*(esteo2$hb)+5.55481)+exp(-331.36213-1.06286*mean(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*mean(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*(esteo2$hb)+7.79220))
y <- data.frame(esteo2$hb,pi_1)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo2$hb,pi_1)$esteo2.hb, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo2.hb,y$pi_1,type='l',xlab="hb 수치", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(10.2,14.2),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=1,lwd=2, col=4)
par(new = T)
pi_2 <- exp(-331.36213-1.06286*mean(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*mean(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*(esteo2$hb)+7.79220)/(1+exp(733.90554-3.12537*mean(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*mean(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*(esteo2$hb)+5.55481)+exp(-331.36213-1.06286*mean(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*mean(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*(esteo2$hb)+7.79220))
y <- data.frame(esteo2$hb,pi_2)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo2$hb,pi_2)$esteo2.hb, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo2.hb,y$pi_2,type='l',xlab="hb 수치", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(10.2,14.2),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=3,lwd=2, col=3)
par(new = T)
pi_3 <- 1/(1+exp(733.90554-3.12537*mean(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*mean(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*(esteo2$hb)+5.55481)+exp(-331.36213-1.06286*mean(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*mean(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*(esteo2$hb)+7.79220))
y <- data.frame(esteo2$hb,pi_3)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo2$hb,pi_3)$esteo2.hb, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo2.hb,y$pi_3,type='l',xlab="hb 수치", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(10.2,14.2),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=5,lwd=2, col=6)
par(new = T)
legend("topright",bty='n', lty=c(1,3,5), c('lscore<q(0.3)','q(0.3)<lscore<q(0.7)','q(0.7)<lscore'), col=c(4,3,6), cex=0.8)
axis(side=1,at=seq(10,15,by=1))
axis(side=2,at=seq(0,1,by=0.2))
title(main= list("fit1_1 / 직업 유 / 운동 유에서 hb", cex= 1, col = "coral",font = 3))
#fit1_1 job:2 (직업무),exer:1 (운동무) 에서 hb 그래프
pi_1 <- exp(733.90554-3.12537*mean(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*mean(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*(esteo2$hb)-9.98673)/(1+exp(733.90554-3.12537*mean(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*mean(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*(esteo2$hb)-9.98673)+exp(-331.36213-1.06286*mean(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*mean(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*(esteo2$hb)-0.51408))
y <- data.frame(esteo2$hb,pi_1)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo2$hb,pi_1)$esteo2.hb, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo2.hb,y$pi_1,type='l',xlab="hb 수치", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(10.2,14.2),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=1,lwd=2, col=4)
par(new = T)
pi_2 <- exp(-331.36213-1.06286*mean(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*mean(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*(esteo2$hb)-0.51408)/(1+exp(733.90554-3.12537*mean(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*mean(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*(esteo2$hb)-9.98673)+exp(-331.36213-1.06286*mean(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*mean(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*(esteo2$hb)-0.51408))
y <- data.frame(esteo2$hb,pi_2)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo2$hb,pi_2)$esteo2.hb, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo2.hb,y$pi_2,type='l',xlab="hb 수치", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(10.2,14.2),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=3,lwd=2, col=3)
par(new = T)
pi_3 <- 1/(1+exp(733.90554-3.12537*mean(esteo2$bmi)+1.19856*mean(esteo2$muscle)-3.41221*mean(esteo2$chid)-5.35798*mean(esteo2$menopage)+0.09814*mean(esteo2$chol)-153.25241*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.70636*mean(esteo2$alt)-24.87064*(esteo2$hb)-9.98673)+exp(-331.36213-1.06286*mean(esteo2$bmi)-1.29775*mean(esteo2$muscle)+0.15450*mean(esteo2$chid)+1.37580*mean(esteo2$menopage)-0.02654*mean(esteo2$chol)+45.00048*mean(esteo2$cr)-0.81237*mean(esteo2$alt)+22.29385*(esteo2$hb)-0.51408))
y <- data.frame(esteo2$hb,pi_3)
y <- y[c(order(data.frame(esteo2$hb,pi_3)$esteo2.hb, decreasing = F)),]
plot(y$esteo2.hb,y$pi_3,type='l',xlab="hb 수치", ylab="Prdicted Probability",xlim=c(10.2,14.2),ylim=c(0,1),xaxt="n",yaxt="n",pch=16, lty=5,lwd=2, col=6)
par(new = T)
legend("topright",bty='n', lty=c(1,3,5), c('lscore<q(0.3)','q(0.3)<lscore<q(0.7)','q(0.7)<lscore'), col=c(4,3,6), cex=0.8)
axis(side=1,at=seq(10,15,by=1))
axis(side=2,at=seq(0,1,by=0.2))
title(main= list("fit1_1 / 직업 무 / 운동 유에서 hb 그래프", cex= 1, col = "coral",font = 3))
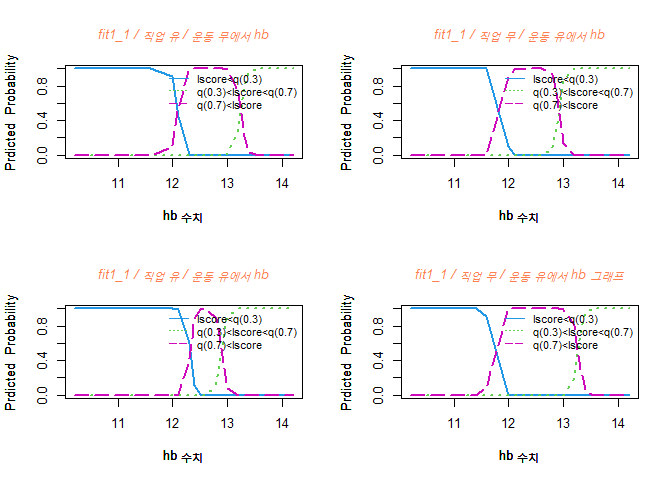
hb 수치가 성인 여성의 경우 12~16g/dl이 정상 범위이다.
정상 범위에서 골밀도 수치가 높은 그룹에 속할 확률이 높으며 hb 수치가 낮아질 수록 골밀도 수치가 낮은 그룹에 속할 확률이 높아진다.
